|
Electric and Electromagnetic (EM) Waves
An Introduction |
|
Prof. David Bernstein |
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |
|
Electric and Electromagnetic (EM) Waves
An Introduction |
|
Prof. David Bernstein |
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |
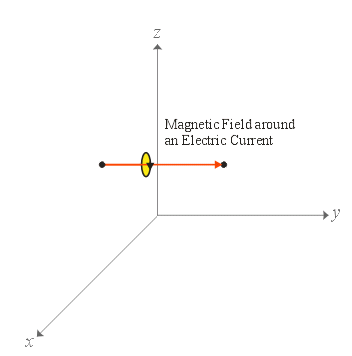
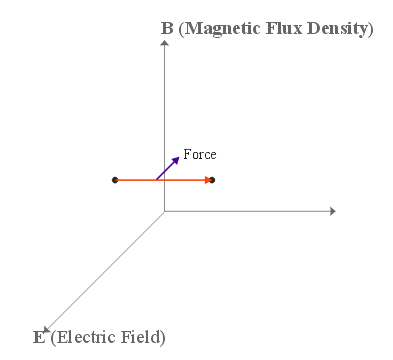
A charge, \(q\), moving with velocity, \(v\), in an electric field, \(E\), and magnetic field, \(B\), experiences a force called the Lorentz force (or electromagnetic force) of:
\(F = qE + qv \times B\)
An Illustration
International Telecommunication Union (ITU) Bands
| Band | Frequency |
| Gamma Rays | 1022 |
| 1021 | |
| 1020 | |
| 1019 | |
| 1018 | |
| 1017 | |
| X-Rays | 1016 |
| Ultraviolet | 1015 |
| Visible Light | 1014 |
| Infrared | 1013 |
| THF | 1012 (1THz) |
| EHF | 1011 |
| SHF | 1010 |
| UHF | 10 9 (1GHz) |
| VHF | 10 8 |
| 10 7 | |
| High | 10 6 (1MHz) |
| Medium | 10 5 |
| Low | 10 4 |
| Very Low | 10 3 (1KHz) |
| 10 2 | |
| Extremely Low | 10 1 |
| 10 0 (1Hz) |