-
Declaration:
- Function arccos(x : float) : float;
-
Description:
- Arccos returns the inverse cosine of its argument x. The argument x should lie between -1
and 1 (borders included).
-
Errors:
- If the argument x is not in the allowed range, an EInvalidArgument exception is raised.
-
See also:
- arcsin (457), arcosh (456), arsinh (459), artanh (459)
Listing: mathex/ex1.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function arcosh(x : float) : float; Function arccosh(x : float) : float;
-
Description:
- Arcosh returns the inverse hyperbolic cosine of its argument x. The argument x should be
larger than 1.
The arccosh variant of this function is supplied for Delphicompatibility.
-
Errors:
- If the argument x is not in the allowed range, an EInvalidArgument exception is raised.
-
See also:
- cosh (460), sinh (485), arcsin (457), arsinh (459), artanh (459), tanh (489)
Listing: mathex/ex3.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function arcsin(x : float) : float;
-
Description:
- Arcsin returns the inverse sine of its argument x. The argument x should lie between -1
and 1.
-
Errors:
- If the argument x is not in the allowed range, an EInvalidArgument exception is raised.
-
See also:
- arccos (456), arcosh (456), arsinh (459), artanh (459)
Listing: mathex/ex2.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function arctan2(x,y : float) : float;
-
Description:
- arctan2 calculates arctan(y/x), and returns an angle in the correct quadrant. The
returned angle will be in the range -
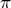 to
to 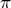 radians. The values of x and y must be between
-2^64 and 2^64, moreover x should be different from zero.
radians. The values of x and y must be between
-2^64 and 2^64, moreover x should be different from zero.
On Intel systems this function is implemented with the native intel fpatan instruction.
-
Errors:
- If x is zero, an overflow error will occur.
-
See also:
- arccos (456), arcosh (456), arsinh (459), artanh (459)
Listing: mathex/ex6.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function arsinh(x : float) : float; Function arcsinh(x : float) : float;
-
Description:
- arsinh returns the inverse hyperbolic sine of its argument x.
The arscsinh variant of this function is supplied for Delphicompatibility.
-
Errors:
- None.
-
See also:
- arcosh (456), arccos (456), arcsin (457), artanh (459)
Listing: mathex/ex4.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function artanh(x : float) : float; Function arctanh(x : float) : float;
-
Description:
- artanh returns the inverse hyperbolic tangent of its argument x, where x should lie in the
interval [-1,1], borders included.
The arctanh variant of this function is supplied for Delphicompatibility.
-
Errors:
- In case x is not in the interval [-1,1], an EInvalidArgument exception is raised.
-
See also:
- arcosh (456), arccos (456), arcsin (457), artanh (459)
-
Errors:
-
-
See also:
Listing: mathex/ex5.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function ceil(x : float) : longint;
-
Description:
- Ceil returns the lowest integer number greater than or equal to x. The absolute value of x
should be less than maxint.
-
Errors:
- If the asolute value of x is larger than maxint, an overflow error will occur.
-
See also:
- floor (463)
Listing: mathex/ex7.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function cosh(x : float) : float;
-
Description:
- Cosh returns the hyperbolic cosine of it’s argument x.
-
Errors:
- None.
-
See also:
- arcosh (456), sinh (485), arsinh (459)
Listing: mathex/ex8.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function cotan(x : float) : float;
-
Description:
- Cotan returns the cotangent of it’s argument x. x should be different from zero.
-
Errors:
- If x is zero then a overflow error will occur.
-
See also:
- tanh (489)
Listing: mathex/ex9.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function cycletorad(cycle : float) : float;
-
Description:
- Cycletorad transforms it’s argument cycle (an angle expressed in cycles) to radians. (1
cycle is 2
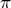 radians).
radians).
-
Errors:
- None.
-
See also:
- degtograd (462), degtorad (463), radtodeg (482), radtograd (482), radtocycle (481)
Listing: mathex/ex10.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function degtograd(deg : float) : float;
-
Description:
- Degtograd transforms it’s argument deg (an angle in degrees) to grads.
(90 degrees is 100 grad.)
-
Errors:
- None.
-
See also:
- cycletorad (461), degtorad (463), radtodeg (482), radtograd (482), radtocycle (481)
Listing: mathex/ex11.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function degtorad(deg : float) : float;
-
Description:
- Degtorad converts it’s argument deg (an angle in degrees) to radians.
(pi radians is 180 degrees)
-
Errors:
- None.
-
See also:
- cycletorad (461), degtograd (462), radtodeg (482), radtograd (482), radtocycle (481)
Listing: mathex/ex12.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function floor(x : float) : longint;
-
Description:
- Floor returns the largest integer smaller than or equal to x. The absolute value of x should
be less than maxint.
-
Errors:
- If x is larger than maxint, an overflow will occur.
-
See also:
- ceil (460)
Listing: mathex/ex13.pp
-
Declaration:
- Procedure frexp(x : float;var mantissa : float; var exponent : integer);
-
Description:
- Frexp returns the mantissa and exponent of it’s argument x in mantissa and exponent.
-
Errors:
- None
-
See also:
Listing: mathex/ex14.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function gradtodeg(grad : float) : float;
-
Description:
- Gradtodeg converts its argument grad (an angle in grads) to degrees.
(100 grad is 90 degrees)
-
Errors:
- None.
-
See also:
- cycletorad (461), degtograd (462), radtodeg (482), radtograd (482), radtocycle (481), gradtorad
(465)
Listing: mathex/ex15.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function gradtorad(grad : float) : float;
-
Description:
- Gradtorad converts its argument grad (an angle in grads) to radians.
(200 grad is pi degrees).
-
Errors:
- None.
-
See also:
- cycletorad (461), degtograd (462), radtodeg (482), radtograd (482), radtocycle (481), gradtodeg
(465)
Listing: mathex/ex16.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function hypot(x,y : float) : float;
-
Description:
- Hypot returns the hypotenuse of the triangle where the sides adjacent to the square angle
have lengths x and y.
The function uses Pythagoras’ rule for this.
-
Errors:
- None.
-
See also:
Listing: mathex/ex17.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function intpower(base : float;exponent : longint) : float;
-
Description:
- Intpower returns base to the power exponent, where exponent is an integer value.
-
Errors:
- If base is zero and the exponent is negative, then an overflow error will occur.
-
See also:
- power (480)
Listing: mathex/ex18.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function ldexp(x : float;p : longint) : float;
-
Description:
- Ldexp returns 2px.
-
Errors:
- None.
-
See also:
- lnxp1 (468), log10 (468),log2 (469),logn (470)
Listing: mathex/ex19.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function lnxp1(x : float) : float;
-
Description:
- Lnxp1 returns the natural logarithm of 1+X. The result is more precise for small values of
x. x should be larger than -1.
-
Errors:
- If x < -1 then an EInvalidArgument exception will be raised.
-
See also:
- ldexp (467), log10 (468),log2 (469),logn (470)
Listing: mathex/ex20.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function log10(x : float) : float;
-
Description:
- Log10 returns the 10-base logarithm of X.
-
Errors:
- If x is less than or equal to 0 an ’invalid fpu operation’ error will occur.
-
See also:
- ldexp (467), lnxp1 (468),log2 (469),logn (470)
Listing: mathex/ex21.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function log2(x : float) : float;
-
Description:
- Log2 returns the 2-base logarithm of X.
-
Errors:
- If x is less than or equal to 0 an ’invalid fpu operation’ error will occur.
-
See also:
- ldexp (467), lnxp1 (468),log10 (468),logn (470)
Listing: mathex/ex22.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function logn(n,x : float) : float;
-
Description:
- Logn returns the n-base logarithm of X.
-
Errors:
- If x is less than or equal to 0 an ’invalid fpu operation’ error will occur.
-
See also:
- ldexp (467), lnxp1 (468),log10 (468),log2 (469)
Listing: mathex/ex23.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function max(Int1,Int2:Cardinal):Cardinal; Function
max(Int1,Int2:Integer):Integer;
-
Description:
- Max returns the maximum of Int1 and Int2.
-
Errors:
- None.
-
See also:
- min (475), maxIntValue (471), maxvalue (472)
Listing: mathex/ex24.pp
-
Declaration:
- function MaxIntValue(const Data: array of Integer): Integer;
-
Description:
- MaxIntValue returns the largest integer out of the Data array.
This function is provided for Delphicompatibility, use the maxvalue (472) function instead.
-
Errors:
- None.
-
See also:
- maxvalue (472), minvalue (476), minIntValue (475)
Listing: mathex/ex25.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function maxvalue(const data : array of float) : float; Function
maxvalue(const data : array of Integer) : Integer; Function maxvalue(const
data : PFloat; Const N : Integer) : float; Function maxvalue(const data :
PInteger; Const N : Integer) : Integer;
-
Description:
- Maxvalue returns the largest value in the data array with integer or float values. The return
value has the same type as the elements of the array.
The third and fourth forms accept a pointer to an array of N integer or float values.
-
Errors:
- None.
-
See also:
- maxIntValue (471), minvalue (476), minIntValue (475)
Listing: mathex/ex26.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function mean(const data : array of float) : float; Function mean(const
data : PFloat; Const N : longint) : float;
-
Description:
- Mean returns the average value of data.
The second form accepts a pointer to an array of N values.
-
Errors:
- None.
-
See also:
- meanandstddev (474), momentskewkurtosis (477), sum (486)
Listing: mathex/ex27.pp
-
Declaration:
- Procedure meanandstddev(const data : array of float; var mean,stddev :
float); procedure meanandstddev(const data : PFloat; Const N : Longint;var
mean,stddev : float);
-
Description:
- meanandstddev calculates the mean and standard deviation of data and returns the result
in mean and stddev, respectively. Stddev is zero if there is only one value.
The second form accepts a pointer to an array of N values.
-
Errors:
- None.
-
See also:
- mean (473),sum (486), sumofsquares (487), momentskewkurtosis (477)
Listing: mathex/ex28.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function min(Int1,Int2:Cardinal):Cardinal; Function
min(Int1,Int2:Integer):Integer;
-
Description:
- min returns the smallest value of Int1 and Int2;
-
Errors:
- None.
-
See also:
- max (470)
Listing: mathex/ex29.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function minIntValue(const Data: array of Integer): Integer;
-
Description:
- MinIntvalue returns the smallest value in the Data array.
This function is provided for Delphicompatibility, use minvalue instead.
-
Errors:
- None
-
See also:
- minvalue (476), maxIntValue (471), maxvalue (472)
Listing: mathex/ex30.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function minvalue(const data : array of float) : float; Function
minvalue(const data : array of Integer) : Integer; Function minvalue(const
data : PFloat; Const N : Integer) : float; Function minvalue(const data :
PInteger; Const N : Integer) : Integer;
-
Description:
- Minvalue returns the smallest value in the data array with integer or float values. The
return value has the same type as the elements of the array.
The third and fourth forms accept a pointer to an array of N integer or float values.
-
Errors:
- None.
-
See also:
- maxIntValue (471), maxvalue (472), minIntValue (475)
Listing: mathex/ex31.pp
-
Declaration:
- procedure momentskewkurtosis(const data : array of float; var
m1,m2,m3,m4,skew,kurtosis : float); procedure momentskewkurtosis(const data
: PFloat; Const N : Integer; var m1,m2,m3,m4,skew,kurtosis : float);
-
Description:
- momentskewkurtosis calculates the 4 first moments of the distribution of valuesin data
and returns them in m1,m2,m3 and m4, as well as the skew and kurtosis.
-
Errors:
- None.
-
See also:
- mean (473), meanandstddev (474)
Listing: mathex/ex32.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function norm(const data : array of float) : float; Function norm(const
data : PFloat; Const N : Integer) : float;
-
Description:
- Norm calculates the Euclidian norm of the array of data. This equals
sqrt(sumofsquares(data)).
The second form accepts a pointer to an array of N values.
-
Errors:
- None.
-
See also:
- sumofsquares (487)
Listing: mathex/ex33.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function popnstddev(const data : array of float) : float; Function
popnstddev(const data : PFloat; Const N : Integer) : float;
-
Description:
- Popnstddev returns the square root of the population variance of the values in the Data
array. It returns zero if there is only one value.
The second form of this function accepts a pointer to an array of N values.
-
Errors:
- None.
-
See also:
- popnvariance (480), mean (473), meanandstddev (474), stddev (485), momentskewkurtosis
(477)
Listing: mathex/ex35.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function popnvariance(const data : array of float) : float; Function
popnvariance(const data : PFloat; Const N : Integer) : float;
-
Description:
- Popnvariance returns the square root of the population variance of the values in the Data
array. It returns zero if there is only one value.
The second form of this function accepts a pointer to an array of N values.
-
Errors:
- None.
-
See also:
- popnstddev (479), mean (473), meanandstddev (474), stddev (485), momentskewkurtosis (477)
Listing: mathex/ex36.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function power(base,exponent : float) : float;
-
Description:
- power raises base to the power power. This is equivalent to exp(power*ln(base)).
Therefore base should be non-negative.
-
Errors:
- None.
-
See also:
- intpower (467)
Listing: mathex/ex34.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function radtocycle(rad : float) : float;
-
Description:
- Radtocycle converts its argument rad (an angle expressed in radians) to an angle in cycles.
(1 cycle equals 2 pi radians)
-
Errors:
- None.
-
See also:
- degtograd (462), degtorad (463), radtodeg (482), radtograd (482), cycletorad (461)
Listing: mathex/ex37.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function radtodeg(rad : float) : float;
-
Description:
- Radtodeg converts its argument rad (an angle expressed in radians) to an angle in degrees.
(180 degrees equals pi radians)
-
Errors:
- None.
-
See also:
- degtograd (462), degtorad (463), radtocycle (481), radtograd (482), cycletorad (461)
Listing: mathex/ex38.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function radtograd(rad : float) : float;
-
Description:
- Radtodeg converts its argument rad (an angle expressed in radians) to an angle in grads.
(200 grads equals pi radians)
-
Errors:
- None.
-
See also:
- degtograd (462), degtorad (463), radtocycle (481), radtodeg (482), cycletorad (461)
Listing: mathex/ex39.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function randg(mean,stddev : float) : float;
-
Description:
- randg returns a random number which - when produced in large quantities - has a Gaussian
distribution with mean mean and standarddeviation stddev.
-
Errors:
- None.
-
See also:
- mean (473), stddev (485), meanandstddev (474)
Listing: mathex/ex40.pp
-
Declaration:
- Procedure sincos(theta : float;var sinus,cosinus : float);
-
Description:
- Sincos calculates the sine and cosine of the angle theta, and returns the result in sinus
and cosinus.
On Intel hardware, This calculation will be faster than making 2 calls to clculatet he sine
and cosine separately.
-
Errors:
- None.
-
See also:
- arcsin (457), arccos (456).
Listing: mathex/ex41.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function sinh(x : float) : float;
-
Description:
- Sinh returns the hyperbolic sine of its argument x.
-
Errors:
-
-
See also:
- cosh (460), arsinh (459), tanh (489), artanh (459)
Listing: mathex/ex42.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function stddev(const data : array of float) : float; Function stddev(const
data : PFloat; Const N : Integer) : float;
-
Description:
- Stddev returns the standard deviation of the values in Data. It returns zero if there is only
one value.
The second form of the function accepts a pointer to an array of N values.
-
Errors:
- None.
-
See also:
- mean (473), meanandstddev (474), variance (491), totalvariance (490)
Listing: mathex/ex43.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function sum(const data : array of float) : float; Function sum(const data
: PFloat; Const N : Integer) : float;
-
Description:
- Sum returns the sum of the values in the data array.
The second form of the function accepts a pointer to an array of N values.
-
Errors:
- None.
-
See also:
- sumofsquares (487), sumsandsquares (488), totalvariance (490) , variance (491)
Listing: mathex/ex44.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function sumofsquares(const data : array of float) : float; Function
sumofsquares(const data : PFloat; Const N : Integer) : float;
-
Description:
- Sumofsquares returns the sum of the squares of the values in the data array.
The second form of the function accepts a pointer to an array of N values.
-
Errors:
- None.
-
See also:
- sum (486), sumsandsquares (488), totalvariance (490) , variance (491)
Listing: mathex/ex45.pp
-
Declaration:
- Procedure sumsandsquares(const data : array of float; var sum,sumofsquares
: float); Procedure sumsandsquares(const data : PFloat; Const N : Integer;
var sum,sumofsquares : float);
-
Description:
- sumsandsquares calculates the sum of the values and the sum of the squares of the values
in the data array and returns the results in sum and sumofsquares.
The second form of the function accepts a pointer to an array of N values.
-
Errors:
- None.
-
See also:
- sum (486), sumofsquares (487), totalvariance (490) , variance (491)
Listing: mathex/ex46.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function tan(x : float) : float;
-
Description:
- Tan returns the tangent of x.
-
Errors:
- If x (normalized) is pi/2 or 3pi/2 then an overflow will occur.
-
See also:
- tanh (489), arcsin (457), sincos (484), arccos (456)
Listing: mathex/ex47.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function tanh(x : float) : float;
-
Description:
- Tanh returns the hyperbolic tangent of x.
-
Errors:
- None.
-
See also:
- arcsin (457), sincos (484), arccos (456)
Listing: mathex/ex48.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function totalvariance(const data : array of float) : float; Function
totalvariance(const data : PFloat; Const N : Integer) : float;
-
Description:
- TotalVariance returns the total variance of the values in the data array. It returns zero if
there is only one value.
The second form of the function accepts a pointer to an array of N values.
-
Errors:
- None.
-
See also:
- variance (491), stddev (485), mean (473)
Listing: mathex/ex49.pp
-
Declaration:
- Function variance(const data : array of float) : float; Function
variance(const data : PFloat; Const N : Integer) : float;
-
Description:
- Variance returns the variance of the values in the data array. It returns zero if there is
only one value.
The second form of the function accepts a pointer to an array of N values.
-
Errors:
- None.
-
See also:
- totalvariance (490), stddev (485), mean (473)
Listing: mathex/ex50.pp
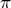 to
to 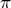 radians. The values of x and y must be between
-2^64 and 2^64, moreover x should be different from zero.
radians. The values of x and y must be between
-2^64 and 2^64, moreover x should be different from zero.
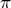 to
to 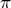 radians. The values of x and y must be between
-2^64 and 2^64, moreover x should be different from zero.
radians. The values of x and y must be between
-2^64 and 2^64, moreover x should be different from zero.
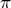 radians).
radians).