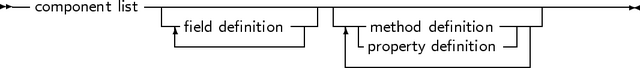
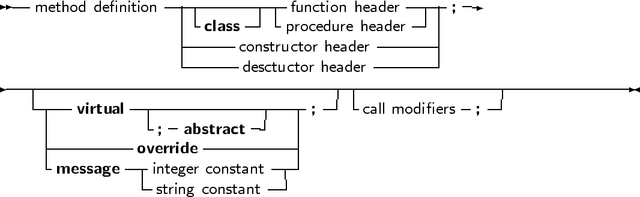
The prototype declaration of a class is as follows :
As many private, protected, published and public blocks as needed can be repeated. Methods
are normal function or procedure declarations. As can be seen, the declaration of a class is almost
identical to the declaration of an object. The real difference between objects and classes is in the
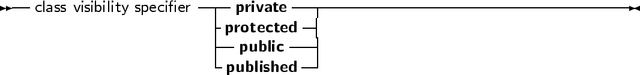
way they are created (see further in this chapter). The visibility of the different sections is as
follows:
-
Private
- All fields and methods that are in a private block, can only be accessed in the
module (i.e. unit) that contains the class definition. They can be accessed from inside
the classes’ methods or from outside them (e.g. from other classes’ methods)
-
Protected
- Is the same as Private, except that the members of a Protected section are
also accessible to descendent types, even if they are implemented in other modules.
-
Public
- sections are always accessible.
-
Published
- Is the same as a Public section, but the compiler generates also type information
that is needed for automatic streaming of these classes. Fields defined in a published
section must be of class type. Array peroperties cannot be in a published section.