
image from http://www.casinocenter.com/rules-strategy-lottery/
|
CS 139 Algorithm Development
PA6: Lottery Checker V2
Part A - Due: Monday, April 20 at 11:59 PM - This will build from PA5-Part B. No separate grade for this step.
Part B - Due: Tuesday, April 28 at 11:59
- -10% on Wednesday, April 29
- -30% on Thursday, April 30
- Not accepted afterwards
Part C - Due: Wednesday, April 29 at 11:59 or 24 hours after successful submission of PartB |
UPDATES:
2/24/2015 - Updates for null arrays for picks or prizes. See RED comments in the validation section.
Objectives
Students will demonstrate:
- they can use a UML Diagram to restructure PA5, Lottery.
- they can create test cases for an Object Oriented component
- they have an understanding of object oriented programming at a beginner level.
Background
Welcome to the world famous JMU Computer
Science lottery! In this assignment, you will implement the
functionality to support a cash drawing, to be redeemed for fabulous
prizes. Your task includes writing methods that: (1)
generate a list of random numbers as specified by a user (quantity
and range) as an array, (2) compare
a "ticket" to the official lottery numbers selected by the contest
administrator, and (3) create an array of prizes given the
size of the "lottery" and total prize money to award.
Your program will prompt the user for the number of numbers and the prize amount. The seed value will come from the command line arguments (or a default used if no arguments are given).
This program is based on Programming Challenges #9 in your Gaddis
textbook --- see Chapter 7 (Watermelon edition) or Chapter 8
(Puzzle edition).
Requirements
Your work will start with the following files:
- Lottery.java -- need to create this file, but you should build on the PA5 file.
- Lottery_Test.java -- need to create this file, but you should build on the PA5 file.
Both Lottery.java and Lottery_Test.java must conform to the CS
139 Style Guide, including documentation. Rules about declaring and initializing on the same line are relaxed as is the rule about declaring everything at the top of the method. All methods should be documented as to their purpose and the class itself should be documented. All names, indentation, and other rules still apply.
Some Definitions
- picks - the winning numbers for a lottery,
represented as an array of integers
- userNumbers - the numbers that the user has
chosen, represented as an array of integers
- prizes - amounts of money to be awarded to
the winners, represented as an array of dollar amounts based on
the number of lottery numbers matched
PART B
The Lottery.java file.
UML of the new version. NOTE: The basic functions that you built before will still be present, but their parameters may change. In addition, some new functionality has been introduced. Note that some of these methods are now private to insure data protection.
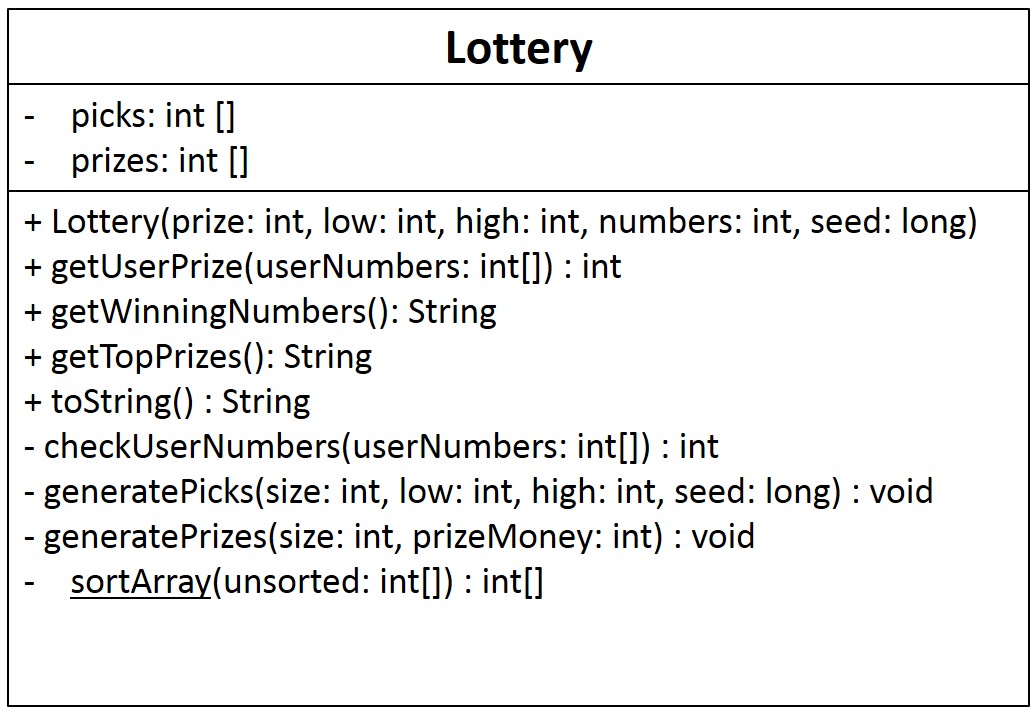
The public methods are called directly by Web-CAT,
so they must be implemented exactly as specified. (Hint: copy-and-paste
them to avoid any typos.) You may add additional methods if you like. Also, for testing, you can always temporarily make the method public, then make it private for final deployment. Just do not build any tests that will test the private methods directly.
Previous methods that have changed
- private int checkUserNumbers(int[]
userNumbers)
- This method has been changed to a private non-static method. checkUserNumbers checks the list of userNumbers against the
numbers in the picks array to count how many lottery numbers
the user guessed correctly. For example, if the picks are {14,
23, 24, 25, 30} and the userNumbers are {5, 19, 14, 25, 17}, the
method should return 2 (because each array in this example
contains both 14 and 25).
-
- private void generatePicks(int size, int
lowValue, int highValue, long seed)
- This method has been changed to a private non-static method that returns nothing. generatePicks will build an array of the given size, and load
it with random numbers from lowValue to highValue inclusively.
No number may be used more than once. The resulting array should
be sorted in ascending order and should be stored in the picks attribute.
NOTE: In order to properly test this method, we will use a seed
value for the random number generator. This will cause the picks
to be "random" in a particular predictable sequence. (This
technique was also used to generate the dictionary words in
PA4). See http://docs.oracle.com/javase/6/docs/api/java/util/Random.html#Random(long) for how this constructor looks.
private void generatePrizes(int size, int
prizeMoney)- This method has been changed to a private non-static method. generatePrizes creates an array of prize amounts based on the
size of the lottery pick and the total prizeMoney. The array
positions correspond to the count of correct numbers in a
lottery pick (zero through size, inclusively).
This array is stored as the attribute, prizes.
The algorithm for generating prize money is as follows. If a
player guesses 0, 1, or 2 numbers correctly the prize amount is
0. The remaining prize money is generated by awarding to each
level (starting with correctly guessing all of the numbers) 3/4
of the available prize money, rounded to the nearest dollar,
with the last count (3 correct) receiving whatever remains. For
example, if the lottery were 6 numbers and the prizeMoney were
1000, 6 correct would get 750, 5 correct would get 3/4 of the
remainder or 188, 4 correct would get 3/4 of the remainder or
47, and 3 correct would get the rest, 15. If there were only 3
numbers and 500 in prize money, 3 matching numbers would get all
500. Note that the prizes array length will be
one more than the count of numbers in the lottery (size), since
it must include the prize for zero and for size.
- private static int[] sortArray(int[] unsorted)
- NOTE: This method has not changed. This method remains static. sortArray takes in an unsorted array and returns a copy of that array sorted in ascending order. This is a helper method
that may be used in generatePicks and/or checkUserNumbers. This
method should not change its parameter. If the unsorted array is null, then this method should return null.
New methods, described
- public Lottery( ... see UML for parameter list)
- This explicit value constructor will use the methods of generatePrizes and generatePicks to load the two attributes prizes and picks. It is possible because of errors that the two arrays could be null. All previous checks for null arrays then should be honored in this and all other methods.
- public int getUserPrize( .. see UML for the paramter list)
- This method will check the userNumbers and return the value of their winnings. If either array is null (picks or userNumbers) then this method should return 0.
- public String getWinningNumbers()
- This method will return a String representation of the picks array. (Use Array.toString()) for the correct formatting). This method should not add any spacing or new line characters to the output.
- public String getTopPrizes()
- This method will return a String of the top prizes in the form:
"Match\tPrize\n"
#\tprize amount\n
There will be one prize line for each non-zero prize.
- public String toString()
- This method will return a String that will display the picks on the first line (using Arrays.toString() format) and the prizes on the second line (using Arrays.toString() format).
Argument Validation
In this assignment, you must check that argument values passed to your
methods are appropriate. Specifically:
- In generatePicks, size must be 3 or greater and no larger than
the range from lowValue to highValue. (Note if highValue is less than lowValue, this rule will also find this anomoly.)
- In checkUserNumbers, both picks and userNumbers cannot be null.
Additionally, they must be the same length.
- In sortArray, unsorted may not be null. If it is, the method should return null.
- In generatePrizes, size must be at least 3 and prizeMoney must
be at least 0.
- In the toString method, if either or both arrays are null, the corresponding line should be the empty String "". There should be a single new line character at the end. (but only one).
- In the getTopPrizes method, if the prize array is null, the method should just return the heading line.
- In getWinningNumbers if the picks array is null, the method should return the empty String.
If any of these conditions do not hold, your methods should return null or -1 (depending on the return type).
Hints
You may find some methods in the java.util.Arrays
class to be helpful. Note however that the Arrays.sort method does
not return a new array. You must implement a copy operation in
your own sort method to ensure that you do not alter the unsorted
array parameters! The Arrays.equals method will be helpful for
testing, in comparing your expected output to the actual output of
your methods that generate arrays.
Deliverables
- Put Lottery.java and Lottery_Test.java in a zip file, and
submit via Web-CAT. Do
not include any other java or class files in your zip file.
- After you complete the assignment, submit a reflection document via Canvas (10 points).
Honor Code
This assignment should be viewed as a take home exam. Your work on
the assignment and your submission must conform to the JMU Honor Code.
Authorized help is limited to the lab handouts, the TAs for any CS
139 or CS 239 section, and the professor for your section. Copying
work from another student or the Internet is an honor code
violation, and will result in a zero on the assignment and possibly
further sanctions. The same is true if you give your code to another
student or post it on the Internet. Your code may be subject to
evaluation by MOSS
(Measure of Software Similarity) which is used to detect
inappropriate similarities among programs.
Updated by nlh 04/22/2015

