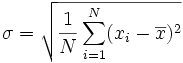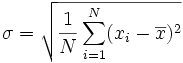CS 139
Algorithm Development
Lab12A: Standard Deviation
Objectives
Students will be able to:
- Read a command line argument
- Redirect input in order to use a file for input instead of the
keyboard
- Read input data into an array
- Use an array to solve a real world problem
Background
Standard deviation is a measure of the spread of a set of values
around a mean. The higher the standard deviation, the more the
values are scattered away from the mean.
To calculate standard deviation, first calculate the mean
(average) of the set, then use that mean to calculate the distance
of each value from the mean. These distances are squared to
account for numbers both less than and greater than the mean
value. Squaring makes all distances positive. The square root
operator is applied after the mean is taken, to rescale the
result. http://www.mathsisfun.com/data/standard-deviation-formulas.html for a further explanation.
This site has a calculator that you can use to check your work: http://www.miniwebtool.com/population-standard-deviation-calculator/
From Wikipedia:
Given a set of N values, x1 through xn,
with mean x, the
standard deviation (σ) is:
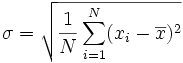
The population standard deviation of a discrete uniform random
variable X can be calculated as follows:
1. For each value xi calculate the difference xi
- x between xi
and the average value x.
2. Calculate the square of each difference, and sum the squares.
3. Find the average of the squared differences. This quantity is
the variance (σ2).
4. Take the square root of the variance to determine the standard
deviation.
Key Terms
- Command line argument - A value passed to a program that is
called from the command line
- Mean - An average
- Standard deviation - A measure of the spread of values around
a mean
Materials
You will write this program from scratch.
You may use the following file for testing: testData.
To use the file, run your program in the command line environment
and override standard input. See demo at the beginning of class
for this technique.
Part 1 General Instructions:
- Setup your program environment. Create a new folder for your
files.
- Download the testData file into the
folder.
- Create two new program file StdDev.java,
and StdDevHelper.java.
Part 2 Creating an array from input values:
You will implement your program in two files, StdDev.java and
StdDevHelper.java. The main function (in StdDev.java)
will read a series of numbers, create an array containing those
numbers, call the mean and standard deviation functions from
StdDevHelper, and then report the results.
- If the main program is passed a command line argument, that
argument will specify the number of values to be read. If no
command line argument is passed, the program should read 25
values. Note that the argument list is an array of Strings. (see
the
Integer.parseInt() method documentation for converting a
string to an integer). Use the following code to do this:
if (args.length > 0)
size = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
else
size = 25;
- Create an array of double that is built to the size of the
command line argument (or 25 as a default if no argument is
provided).
- To read the input values, use a loop which will read the
values from the keyboard (as doubles) and store them in the
array. No prompt should be output before reading the
values. The loop should terminate when the appropriate number of
values has been read.
- Once the array is built, pass it to functions in StdDevHelper.java.
- Output the values as a single line, "Mean:
%.2f\n", containing the calculated mean value. This
output should be performed by StdDev.java.
- In order to test your program at this point, create a "stub"
for the method described in Part 3. (A stub is an empty
method that returns zero or null.)
- To test the program using the command line argument for the
number of values to read in, go to the terminal window, navigate
to your work folder, and enter:
java StdDev 25
This command will run the StdDev program passing 25 as the
command line argument to the main method. If you run it with
just java StdDev, then the default of 25 values
should be used.
Part 3 Creating a method to calculate the mean.
- In the StdDevHelper.java file,
create a function (a static method), mean,
that will take an array of double values as its parameter,
and then calculate and return the mean of those numbers.
- The method should insure that the array is not null and that
it has more than 0 elements. If either of these conditions
exists, the method should return 0.
- Test your mean method from the StdDev.java program. See Part
2- step 8 for using the command line and passing in the
appropriate number of values (use a small number of values so
you can check your mean easily).
Part 4 Calculating the Standard deviation:
- Add to StdDevHelper a function, stdDev,
that computes the standard deviation of a passed array of double numbers. See the formula above in
the Background section.
- Your standardDeviation function should use the mean function created in Part 3 above.
- The method should ensure that the array is not null and that
it has more than 0 elements. If either of those conditions
exists, return -1.
- Add to the StdDev program a single line of output following
the mean output line. The format of the standard deviation line
should be "Standard Deviation: %.2f\n".
- Test your program.
Part 5 Redirecting input:
By now you are probably tired of typing in all the values during
testing. Wouldn't it be nice to just have a file that you could use
for testing, so that you could set it up once and then use it
repeatedly? Without changing the program, you can!
- If you have not already done so, download the testData.txt
file into the folder containing your program.
- Go to the terminal window and navigate to your work folder.
- At the command line, type the command
java StdDev 25
<testData.txt. This command is interpreted as run
StdDev using 25 for the command line argument and redirect
input to use testData.txt instead of the normal
System.in.
The redirect operator (<) is a tool of the command shell,
which is the program that is reading and processing the commands
that you enter in the terminal window. It's also possible to
redirect the output of your program to a file, using the >
symbol, as in: java StdDev 25
<testData.txt >save_output.txt
Part 6 Turning in your work:
Submit this program to WebCAT for accuracy checking.
Part 7 - Optional - Coding Bat Practice with Arrays
- Arrays-2, countEvens: http://codingbat.com/prob/p162010
- Arrays-2, matchUp: http://codingbat.com/prob/p136254