|
Scientific Visualization and Animation: Examples from Geography
|
|
Prof. David Bernstein |
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |
|
Scientific Visualization and Animation: Examples from Geography
|
|
Prof. David Bernstein |
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |
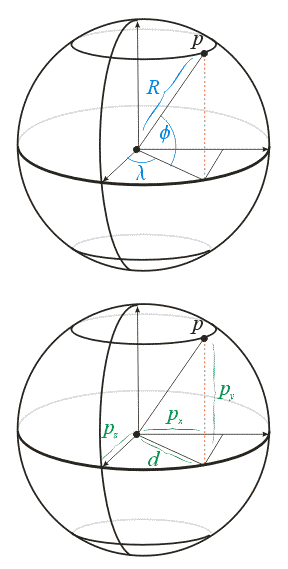
Notation
/**
* Convert from spherical longitude/latitude to
* 3D rectangular coordinates (with the origin at the
* center of the sphere)
*
* @param lon The longitude in degrees (IN)
* @param lat The latitude in degrees (IN)
* @param x The x-coordinate (OUT)
* @param y The y-coordinate (OUT)
* @param x The z-coordinate (OUT)
*/
void lonlat2xyz(double lon, double lat, double &x, double &y, double &z)
{
double coslat, coslon, sinlat, sinlon;
coslat = cos(lat*RADIANS_PER_DEGREE);
coslon = cos(lon*RADIANS_PER_DEGREE);
sinlat = sin(lat*RADIANS_PER_DEGREE);
sinlon = sin(lon*RADIANS_PER_DEGREE);
x = (coslat * sinlon);
y = (sinlat);
z = (coslat * coslon);
}
#ifndef FEATURE_C
#define FEATURE_C
/**
* A generic geographic feature (e.g., a polygon, piecewise linear curve)
*
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
* @version 1.0
*/
struct feature
{
int id; // Unique identifier
char *type; // POLYGON, LINE_STRIP, ...
int size; // Number of vertices
double *lon; // Longitudes
double *lat; // Latitudes
double *x; // Cartesian x-coordinate
double *y; // Cartesian y-coordinate
double *z; // Cartesian z-coordinate
double *xProj; // Projected x-coordinate (for maps)
double *yProj; // Prohected y-coordinate (for maps)
};
#endif
/**
* Create the array of features, read the countries from
* the file, create the polygons, and insert them
* into the array of features
*
* @return The index of the next empty feature
*/
int readPolygons()
{
char name[80];
double lat, lon;
feature *f;
FILE *in;
int countryNumber, k, numberOfCountries;
int numberOfPolygons, polygonNumber, size;
in = fopen("world.txt", "r");
fscanf(in, "%d,%d", &numberOfPolygons, &numberOfCountries);
numberOfFeatures = numberOfPolygons + GRID_SIZE;
features = new feature[numberOfFeatures];
for (k=0; k<numberOfPolygons; k++)
{
fscanf(in, "%d,%d,%d,%s", &polygonNumber, &countryNumber, &size, name);
f = new feature;
initializeFeature(f, size);
f->id = countryNumber;
f->type = "POLYGON";
f->size = size;
for (int i=0; i<size; i++)
{
fscanf(in, "%lf,%lf", &lon, &lat);
setCoordinate(f, i, lon, lat);
}
features[k] = *f;
}
fclose(in);
return k;
}
/**
* Create the lines that comprise the longitude/latitude
* grid and insert them into the array of features
*
* @param firstIndex The index to use for the first line
*/
void createGrid(int firstIndex)
{
feature *f;
int k, size;
k = firstIndex;
// Create the longitude lines
for (int lon=-180; lon<=180; lon+=10) // 37 lines
{
size = 19;
f = new feature;
initializeFeature(f, size);
f->id = 214;
f->type = "LINE_STRIP";
f->size = size;
int i = 0;
for (int lat=-90; lat<=90; lat+=10)
{
setCoordinate(f, i, (double)lon, (double)lat);
i++;
}
features[k] = *f;
k++;
}
// Create the latitude lines
for (int lat=-90; lat<=90; lat+=10) // 19 lines
{
size = 37;
f = new feature;
initializeFeature(f, size);
f->id = 214;
f->type = "LINE_STRIP";
f->size = size;
int i = 0;
for (int lon=-180; lon<=180; lon+=10)
{
setCoordinate(f, i, (double)lon, (double)lat);
i++;
}
features[k] = *f;
k++;
}
}
/**
* Display the Earth
*/
void onDisplay()
{
feature *f;
GLenum type;
GLfloat v[3];
for (int i=0; i<numberOfFeatures; i++)
{
// Get the Feature
f = &features[i];
// Determine the Feature's type
if (strcmp(f->type, "POLYGON") == 0) type = GL_POLYGON;
else if (strcmp(f->type, "LINE_STRIP") == 0) type = GL_LINE_STRIP;
else type = GL_POINTS;
// Begin the graphics primitive
glBegin(type);
{
glColor3fv(colors[f->id]);
for (int j=0; j<f->size; j++)
{
// Use the 3D rectangular coordinates
v[0] = f->x[j];
v[1] = f->y[j];
v[2] = f->z[j];
glVertex3fv(v);
}
}
glEnd();
}
}
/**
* The entry point of the application.
*
* @param argc The number of command line arguments
* @param argv The array of command line arguments
* @return A status code
*/
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
float min[] = {-3.0, -3.0, -3.0};
float max[] = { 3.0, 3.0, 3.0};
int k;
// Create the array of colors
initializeColors();
// Create the Feature set
k = readPolygons();
createGrid(k);
// Create and initialize the SVA window
svaCreate(argc, argv, min, max);
svaShowAxes(false);
// Start the SVA visualization
svaStartVisualization();
}
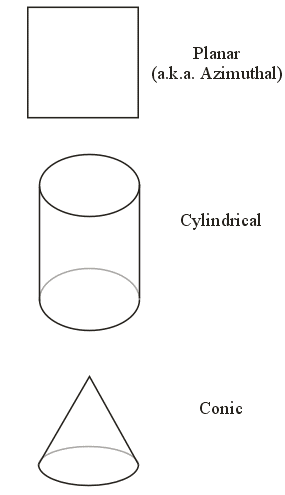
Projection Surfaces
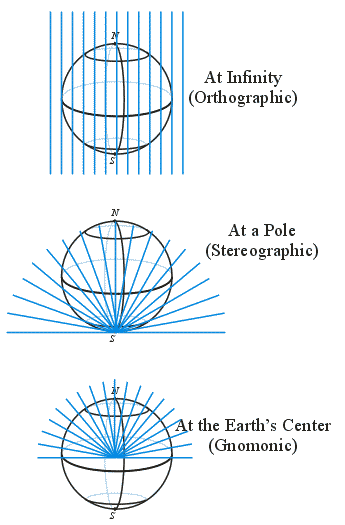
Light Sources
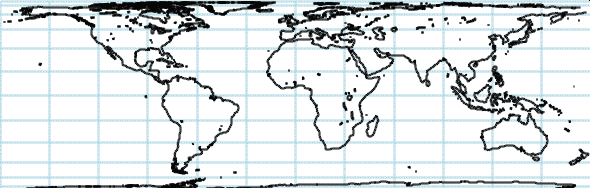
The World
/**
* Project from spherical longitude/latitude to
* 2D rectangular coordinates (with the origin at the
* equator and Greenwich meridian)
*
* @param lon The longitude in degrees (IN)
* @param lat The latitude in degrees (IN)
* @param x The x-coordinate (OUT)
* @param y The y-coordinate (OUT)
*/
void cylindricalEqualArea(double lon, double lat, double &x, double &y)
{
x = lon*RADIANS_PER_DEGREE;
y = sin(lat*RADIANS_PER_DEGREE);
}
/**
* Display the Earth
*/
void onDisplay()
{
feature *f;
GLenum type;
GLfloat v[3];
for (int i=0; i<numberOfFeatures; i++)
{
// Get the Feature
f = &features[i];
// Determine the Feature's type
if (strcmp(f->type, "POLYGON") == 0) type = GL_POLYGON;
else if (strcmp(f->type, "LINE_STRIP") == 0) type = GL_LINE_STRIP;
else type = GL_POINTS;
// Begin the graphics primitive
glBegin(type);
{
glColor3fv(colors[f->id]);
for (int j=0; j<f->size; j++)
{
// Use the projected coordinates
v[0] = f->xProj[j];
v[1] = f->yProj[j];
v[2] = 0.0;
glVertex3fv(v);
}
}
glEnd();
}
}