|
The Strategy Pattern
An Introduction with Examples in Java |
|
Prof. David Bernstein |
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |
|
The Strategy Pattern
An Introduction with Examples in Java |
|
Prof. David Bernstein |
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |
In UML
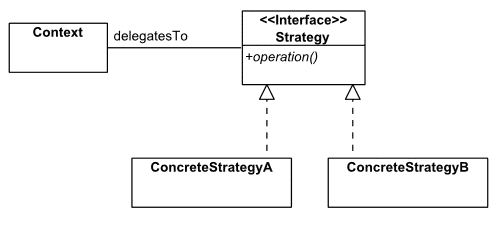
In UML
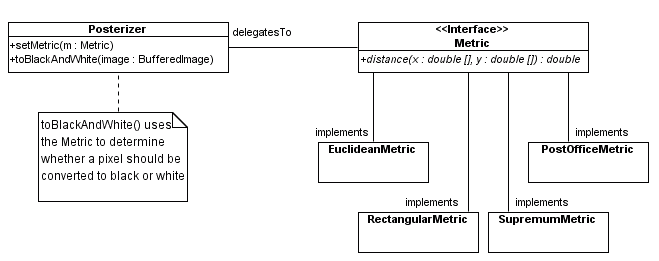
package math;
/**
* A Metric is a function that satisfies the following properties
* for all a, b, c:
*
* distance(a,b) >= 0
* distance(a,b) == 0 iff a == b
* distance(a,b) == distance(b,a)
* distance(a,b) <= distance(a,c) + distance(b,c)
*
* (The last of these properties is called the triangle inequality.)
*
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
* @version 1.0
*/
public interface Metric
{
/**
* Calculate the distance between two n-dimensional points
*
* @param a One n-dimensional point
* @param b Another n-dimensional point
* @return The distance
*/
public abstract double distance(double[] a, double[] b);
}
package math;
/**
* The Euclidean metric (i.e., the notion of distance that
* most people are familiar with)
*
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
* @version 1.0
*/
public class EuclideanMetric
implements Metric
{
/**
* Calculate the distance between two n-dimensional points
* (required by Metric)
*
* Note: For simplicity, this method does not confirm that the
* two arrays are the same size. It uses the smaller size.
*
* @param a One n-dimensional point
* @param b Another n-dimensional point
* @return The distance
*/
public double distance(double[] a, double[] b)
{
double result;
int n;
result = 0.0;
n = Math.min(a.length, b.length);
for (int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
result += Math.pow(a[i]-b[i], 2.0);
}
return Math.sqrt(result);
}
}
package math;
/**
* The rectilinear metric (i.e., the sum of the absolute values of the
* differences between the elements). This is sometimes also
* called the Manhattan metric (because it is the distance you have to walk
* between two points in a city that is layed out on a grid).
*
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
* @version 1.0
*/
public class RectilinearMetric
implements Metric
{
/**
* Calculate the distance between two n-dimensional points
* (required by Metric)
*
* Note: For simplicity, this method does not confirm that the
* two arrays are the same size. It uses the smaller size.
*
* @param a One n-dimensional point
* @param b Another n-dimensional point
* @return The distance
*/
public double distance(double[] a, double[] b)
{
double result;
int n;
result = 0.0;
n = Math.min(a.length, b.length);
for (int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
result += Math.abs(a[i]-b[i]);
}
return result;
}
}
package math;
/**
* The supremum metric. This is sometimes also
* called the uniform metric and/or the infinity metric.
*
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
* @version 1.0
*/
public class SupremumMetric
implements Metric
{
/**
* Calculate the distance between two n-dimensional points
* (required by Metric)
*
* Note: For simplicity, this method does not confirm that the
* two arrays are the same size. It uses the smaller size.
*
* @param a One n-dimensional point
* @param b Another n-dimensional point
* @return The distance
*/
public double distance(double[] a, double[] b)
{
double result, term;
int n;
result = Math.abs(a[0]-b[0]);
n = Math.min(a.length, b.length);
for (int i=1; i<n; i++)
{
term = Math.abs(a[i]-b[i]);
if (term > result) result = term;
}
return result;
}
}
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.image.*;
import math.*;
/**
* A Posterizer reduces the number of colors in an image
*
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
* @version 1.0
*/
public class Posterizer
{
private double[] aa, bb;
private Metric metric;
private static final int[] BLACK = { 0, 0, 0};
private static final int[] WHITE = {255,255,255};
/**
* Default Constructor
*/
public Posterizer()
{
aa = new double[3];
bb = new double[3];
}
/**
* Determine the distance between two colors
*
* @param a The RGB values of one color
* @param b The RGB values of the other color
* @return The distance
*/
private double distance(int[] a, int[] b)
{
double result;
for (int i=0; i<3; i++)
{
aa[i] = a[i];
bb[i] = b[i];
}
result = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
if (metric != null) result = metric.distance(aa, bb);
return result;
}
/**
* Set the Metric to use to determine the distance
* between colors
*
* @param metric The Metric to use
*/
public void setMetric(Metric metric)
{
this.metric = metric;
}
/**
* Convert an image to black-and-white (NOT gray scale)
*
* @param image The BufferedImage to convert
*/
public void toBlackAndWhite(BufferedImage image)
{
ColorModel colorModel;
double blackDistance, whiteDistance;
int height, packedPixel, packedBlack, packedWhite, width;
int[] pixel;
pixel = new int[3];
height = image.getHeight();
width = image.getWidth();
colorModel = image.getColorModel();
packedBlack = colorModel.getDataElement(BLACK,0);
packedWhite = colorModel.getDataElement(WHITE,0);
for (int x=0; x<width; x++)
{
for (int y=0; y<height; y++)
{
packedPixel = image.getRGB(x, y);
colorModel.getComponents(packedPixel, pixel, 0);
blackDistance = distance(pixel, BLACK);
whiteDistance = distance(pixel, WHITE);
if (blackDistance < whiteDistance)
image.setRGB(x, y, 0x00000000);
else
image.setRGB(x, y, 0xFFFFFFFF);
}
}
}
}