|
Customizing TCP Sockets
An Introduction with Examples in Java |
|
Prof. David Bernstein |
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |
|
Customizing TCP Sockets
An Introduction with Examples in Java |
|
Prof. David Bernstein |
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |
| Offset | Size | Type |
| 0 | 1 | '*' (i.e., the ASCII literal *) |
| 1 | 1 | Frame Type |
| 2 | 2 | Sequence Number |
| 4 | 2 | Data Length |
| Code | Frame Type |
| 1 | SIGNON |
| 2 | DATA |
| 3 | ERROR (For future use) |
| 4 | SIGNOFF (For future use) |
| 5 | KEEP_ALIVE (For future use) |
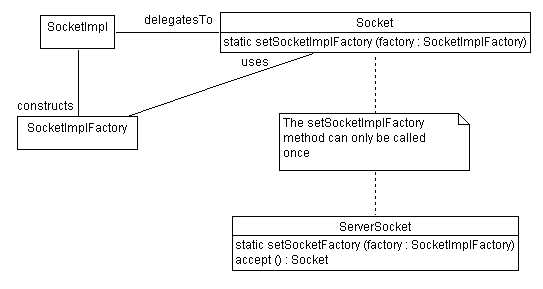
Socket class uses streams, so we need
to take that into considerationSocket
Socket,
we're adding functionality to the stream
import java.io.*;
/**
* For reading input streams using the SFP protocol
*
* @version 1.0
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James madison University
*/
public class SFPInputStream extends InputStream
{
protected int available, dataLength;
protected int frameType, sequenceNumber;
protected DataInputStream in;
/**
* Construct a new SFPInputStream
*
* @param in The InputStream to use
*/
public SFPInputStream(InputStream in)
{
this.in = new DataInputStream(in);
available = 0;
}
/**
* Returns the number of bytes available without blocking
*
*/
public int available() throws IOException
{
return available;
}
/**
* Decode an array of bytes
*
* This version does nothing
*/
protected void decode(byte[] b)
{
// Do nothing
}
/**
* Get the frame type of the most recently/current message
* (See SFPConnection for valid frame types)
*
* @return The frame type
*/
public int getFrameType()
{
return frameType;
}
/**
* Closes this input stream
*/
public void close() throws IOException
{
in.close();
}
/**
* Tests if this input stream supports the mark and reset methods
*/
public boolean markSupported()
{
return false;
}
/**
* Reads the next byte of data
*/
public int read() throws IOException
{
byte[] b;
int retval;
b = new byte[1];
if (available == 0) readHeader();
retval = read(b,0,1);
if (retval > 0) retval = (int)(b[0]);
return retval;
}
/**
* Reads an array of bytes
*
* @param b The buffer into which the data are read
* @param off The start offset of the data
* @param len The maximum number of bytes read
*
* @return The number of bytes actually read or -1 if end-of-stream
*/
public int read(byte[] b, int off, int len) throws IOException
{
byte[] tmp;
int bytesRead, i, length;
if (available == 0) readHeader();
if (len < available) length = len;
else length = available;
tmp = new byte[length];
bytesRead = in.read(tmp);
// For future use
decode(tmp);
if (bytesRead < 0) available = 0;
else
{
available -= bytesRead;
for (i=0; i < bytesRead; i++)
{
b[i+off] = tmp[i];
}
}
return bytesRead;
}
/**
* Reads an array of bytes
*
* @param b The buffer into which the data are read
* @return The number of bytes actually read or -1 if end-of-stream
*/
public int read(byte[] b) throws IOException
{
if (available == 0) readHeader();
return read(b, 0, b.length);
}
/**
* Read the SFP header information
*/
protected void readHeader() throws IOException
{
byte[] b;
char asterisk;
b = new byte[2];
asterisk = (char)(in.readByte());
frameType = (int)(in.readByte());
sequenceNumber = (int)(in.readShort());
dataLength = (int)(in.readShort());
available = dataLength;
}
/**
* Skips over and discards a given number of bytes
*
* Note: Even though n is passed as a long, it is treated as an int
*
* @param n The number of bytes to skip
*/
public long skip(long n) throws IOException
{
byte[] tmp;
int k;
k = (int)n;
tmp = new byte[k];
return read(tmp);
}
}
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
/**
* For writing output streams using the SFLP protocol
*
* Note that all write operations are buffered.
* The actual writing does not take place until
* the flush method is called.
*
* @version 1.0
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James madison University
*/
public class SFPOutputStream extends OutputStream
{
protected int sequenceNumber;
protected DataOutputStream out;
protected LinkedList buffer;
/**
* Construct a new SFPOutputStream
*
* @param out The OutputStream to use
*/
public SFPOutputStream(OutputStream out)
{
this.out = new DataOutputStream(out);
sequenceNumber = 1;
buffer = new LinkedList();
}
/**
* Closes this Output stream (after first
* calling flush);
*/
public void close() throws IOException
{
flush();
out.close();
}
/**
* Flushes this Output stream
*/
public void flush() throws IOException
{
byte b;
Byte byteObject;
ListIterator e;
// Write the header
writeHeader(SFPConnection.DATA, buffer.size());
// Write the contents of the buffer
e = buffer.listIterator();
while (e.hasNext())
{
byteObject = (Byte)e.next();
b = byteObject.byteValue();
out.write(b);
}
// Flush the output stream
out.flush();
// Clear the buffer
buffer.clear();
}
/**
* Writes a single byte of data
*
* @param b The byte to write
*/
protected void write(byte b) throws IOException
{
buffer.addLast(new Byte(b));
}
/**
* Writes a single byte of data
*
* @param b The 1-byte integer to write
*/
public void write(int b) throws IOException
{
write((byte)b);
}
/**
* Writes an array of bytes
*
* @param b The bytes to write
* @param off The start offset of the data
* @param len The maximum number of bytes read
*/
public void write(byte[] b, int off, int len) throws IOException
{
int i;
for (i=0; i < len; i++) write(b[i+off]);
}
/**
* Writes an array of bytes
*
* @param b The bytes to write
*/
public void write(byte[] b) throws IOException
{
int i;
for (i=0; i < b.length; i++) write(b[i]);
}
/**
* Write the SFP header information
*
* @param frameType The frame type
* @param length The length
*/
protected void writeHeader(int frameType, int length) throws IOException
{
out.writeByte((int)('*'));
out.writeByte(frameType);
out.writeShort(sequenceNumber);
out.writeShort(length);
sequenceNumber++;
}
/**
* Write a SIGNON header
*/
protected void writeSIGNON() throws IOException
{
writeHeader(SFPConnection.SIGNON, 0);
out.flush();
}
}
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
/**
* A Socket that uses the SFP protocol
*
* @version 1.0
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
*/
public class SFPSocket extends Socket
{
protected SFPInputStream in;
protected SFPOutputStream out;
/**
* Constructor for server-side sockets
*/
public SFPSocket() throws SocketException
{
super();
in = null;
out = null;
}
/**
* Explicit value constructor for client-side sockets
*
* @param host The host name
* @param port The host port
*/
public SFPSocket(String host, int port) throws IOException
{
super(host, port);
// Start the client side of the sign-on process
DataOutputStream os;
int i;
InputStream is;
is = super.getInputStream();
in = new SFPInputStream(is);
os = new DataOutputStream(super.getOutputStream());
// Write initial message (with header)
//
os.writeByte((int)('*'));
os.writeByte(SFPConnection.SIGNON);
os.writeShort(0);
os.writeShort(SFPConnection.sfpon.length);
os.write(SFPConnection.sfpon, 0, SFPConnection.sfpon.length);
os.flush();
// Read the SIGNON frame from the host
// (in binary; network byte order)
//
in.readHeader();
if (in.getFrameType() != SFPConnection.SIGNON) {
throw(new IOException("No SIGNON from host"));
}
}
/**
* Returns an input stream for this socket
*/
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException
{
if (in == null) in = new SFPInputStream(super.getInputStream());
return in;
}
/**
* Returns an output stream for this socket
*/
public OutputStream getOutputStream() throws IOException
{
if (out == null) out = new SFPOutputStream(super.getOutputStream());
return out;
}
}
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
/**
* A Socket that uses the SFP protocol
*
* @version 1.0
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
*/
public class SFPServerSocket extends ServerSocket
{
/**
* Default Constructor
*/
public SFPServerSocket() throws IOException
{
super(SFPConnection.DEFAULT_PORT);
}
/**
* Listens for a connection to be made to this socket and
* accepts it. The method blocks until a connection is made.
*/
public Socket accept() throws IOException
{
boolean ok;
byte[] initial;
int i, len;
SFPInputStream in;
SFPOutputStream out;
SFPSocket socket;
socket = new SFPSocket();
// Complete the connection (see the javadocs)
implAccept(socket);
// Start the server side of the sign-on process
in = (SFPInputStream)socket.getInputStream();
out = (SFPOutputStream)socket.getOutputStream();
// Read the initial message from the client
initial = new byte[9];
in.read(initial);
// Check the initial message and reply
ok = true;
i = 0;
while ( (i < initial.length))
{
if (initial[i] != SFPConnection.sfpon[i]) ok = false;
i++;
}
if (ok) out.writeSIGNON();
else throw(new IOException("No SFPON from client"));
return socket;
}
}
Use a Factory