|
The Proxy Pattern
An Introduction with Examples in Java |
|
Prof. David Bernstein |
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |
|
The Proxy Pattern
An Introduction with Examples in Java |
|
Prof. David Bernstein |
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |
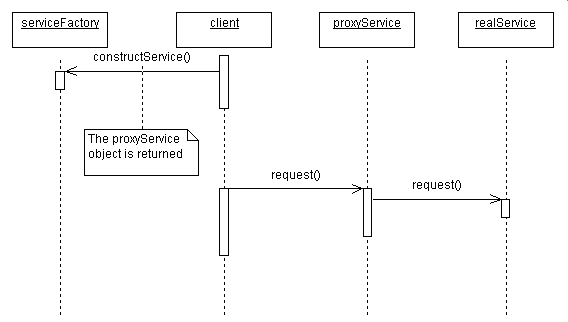
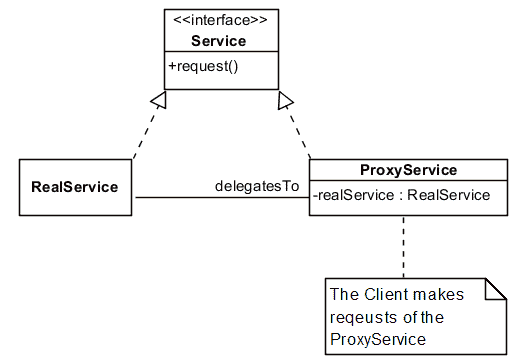
One Approach (in UML)
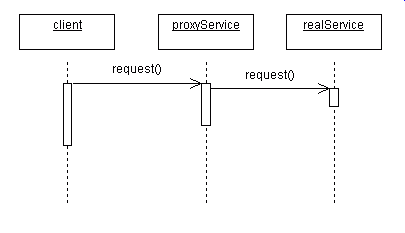
A UML Sequence Diagram
import java.awt.*;
import java.net.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* A proxy for an Icon (an example of the Proxy pattern)
*
* @version 1.0
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
*/
public class IconProxy implements Icon
{
private boolean isLoaded, shouldLoad;
private Image image;
private ImageIcon realIcon;
private int height, width;
private Toolkit toolkit;
private URL url;
private static final int IMAGE_ID = 1;
/**
* Explicit Value Constructor
*
* @param file The name of the file containing the image
* @param width The default width of the image
* @param height The default height of the image
*/
public IconProxy(String file, int width, int height)
{
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
image = null;
realIcon = null;
isLoaded = false;
toolkit = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit();
try
{
url = new URL(file);
shouldLoad = true;
}
catch (MalformedURLException mue)
{
shouldLoad = false;
}
}
/**
* Get the height in pixels (required by Icon)
*
* @return The height (in pixels)
*/
public int getIconHeight()
{
if (isLoaded) return realIcon.getIconHeight();
else return height;
}
/**
* Get the width in pixels (required by Icon)
*
* @return The width (in pixels)
*/
public int getIconWidth()
{
if (isLoaded) return realIcon.getIconWidth();
else return width;
}
/**
* Draw the icon at the specified location (required by Icon)
*
* @param c The Component the Icon is being drawn on
* @param g The Graphics context
* @param x The horizontal position of the upper-left corner
* @param y The vertical position of the upper-left corner
*/
public void paintIcon(Component c, Graphics g, int x, int y)
{
// Get the Image if necessary
if (shouldLoad && image == null) image = toolkit.createImage(url);
// If the URL is ok, check the status of the Image
if (shouldLoad)
{
if (image.getWidth(c) >= 0) isLoaded = true;
}
if(isLoaded) // Delegate to the real Icon
{
if (realIcon == null) realIcon = new ImageIcon(image);
realIcon.paintIcon(c, g, x, y);
}
else // Draw a border
{
g.setColor(Color.black);
g.drawString("Image", x+width/2, y+height/2);
}
}
}
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* A frame that contains an Icon
*
* @version 1.0
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
*/
public class IconFrame extends JFrame
{
private Icon icon;
/**
* Explicit Value Constructor
*
* @param icon The Icon
*/
public IconFrame(Icon icon)
{
this.icon = icon;
}
/**
* Paint this Component
*
* @param g The Graphics context
*/
public void paint(Graphics g)
{
super.paint(g);
icon.paintIcon(this, g, 0, 0);
}
}
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* An example that uses IconProxy (an example of the Proxy pattern)
*
* @version 1.0
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
*/
public class Driver
{
/**
* The entry point
*
* @param args The command-line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Icon icon;
IconFrame frame;
// For example: http://www.lib.jmu.edu/special/SCPix/cav85+/cav85+2.jpg
icon = new IconProxy(args[0],200,200);
frame = new IconFrame(icon);
frame.setSize(400,400);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
In UML