|
Arrays
An Introduction with Examples in Java |
|
Prof. David Bernstein |
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |
|
Arrays
An Introduction with Examples in Java |
|
Prof. David Bernstein |
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |
double income1, income2, income3, income4, income5, income6, income7;
income1 = 550.75;
income2 = 25.60;
income3 = 347.10;
income4 = 120.45;
income5 = 885.00;
income6 = 10.99;
income7 = 123.45;
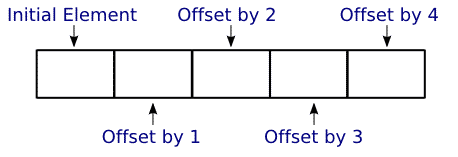
An array is a contiguous block of memory that can be used to hold a fixed number of homogeneous elements.
[]
Modifier:
int[] income;
[]
Operator:
income[5] = 250000;
total = income[3];
One can declare an array and assign all of the elements to it using an "array literal" (formally, an array initializer) as follows:
char[] course = {'C','S','1','3','9'};
int[] age = {18, 21, 65};
One can then assign elements or access elements using the []
operator.
One can declare an array and assign default values to all of the elements to it as follows:
char[] course;
int[] age;
course = new char[5]; \\ Each element is initialized to '\0'
age = new int[3]; \\ Each element is initialized to 0
One can then assign elements or access elements using the []
operator.
double[] income;
income = new double[7];
income[0] = 550.75;
income[1] = 25.60;
income[2] = 347.10;
income[3] = 120.45;
income[4] = 885.00;
income[5] = 10.99;
income[6] = 123.45;
int day;
double bad;
day = 2;
bad = income[day];
// Declare the array
Color[] usFlag;
// Construct/instantiate the array (i.e., allocate memory for 3 references)
usFlag = new Color[3];
// Construct/instantiate each of the elements of the array
usFlag[0] = new Color(204, 0, 0); // Red
usFlag[1] = new Color(255, 255, 255); // White
usFlag[2] = new Color( 0, 0, 204); // Blue
ArrayIndexOutOfBounds "error" will be
generated)x = payment(income[0]);
payment(int[] income)
main(String[] args)
y = payment(taxableIncome);
public int[] schedule(){...}
length contains the number of elements (and
is initialized when memory is allocated)clone() makes a (shallow) copylength Attribute
int n;
int[] strikeouts;
strikeouts = new int[9];
// This will work
n = strikeouts.length;
// This will not work because the length attribute
// is declared to be final (which means it cannot be
// changed after it is initialized)
//
strikeouts.length = 5;
List is used to provide this kind of
functionalityList literals are written using
[ and ] (not {
and })List can be obtained
using the len() function-1 can be used to
work with the last element of the List
: in the "index" (e.g., data[2:5])in operator can be used to
determine if a List contains a particular elementList
can be changed using the append(), insert(),
extend(), and remove() methods