|
One-Dimensional Optimization
An Introduction with Examples |
|
Prof. David Bernstein |
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |
|
One-Dimensional Optimization
An Introduction with Examples |
|
Prof. David Bernstein |
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |
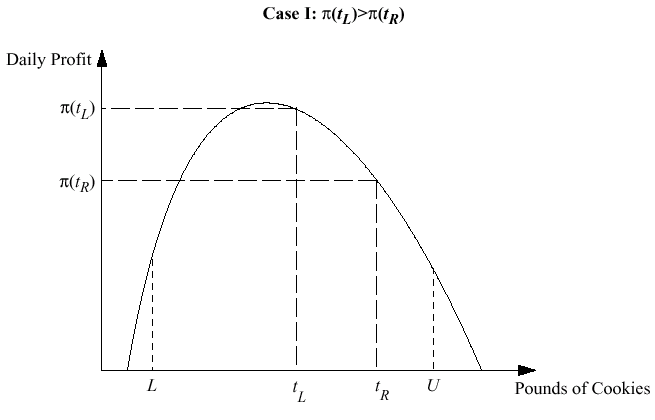
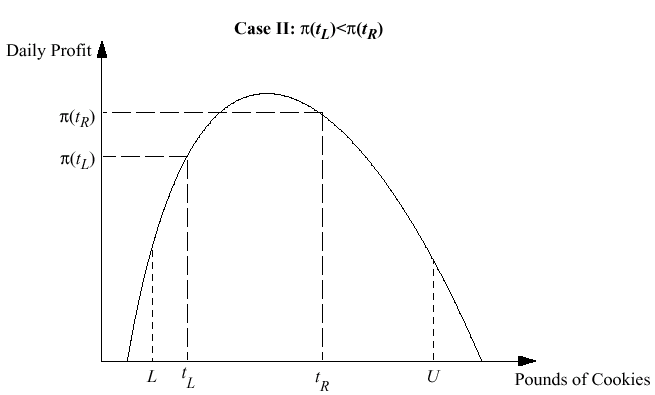
Choose an initial lower bound L and upper bound U
Set t_L equal to L + 0.382 * (U - L)
Set t_R equal to L + 0.618 * (U - L)
while (U - L is too large} {
if (The objective function evaluated at t_L is greater
than the objective function evaluated at t_R) {
Set U equal to t_R
Set t_R equal to t_L
Set t_L equal to L + 0.382 * (U - L)
} else {
Set L equal to t_L
Set t_L equal to t_R
Set t_R equal to L + 0.618 * (U - L)
}
}
| Iter. | L | tL | tR | U |
| 1 | 0.00 | 305.57 | 494.43 | 800.00 |
| 2 | 0.00 | 188.85 | 305.57 | 494.43 |
| 3 | 188.85 | 305.57 | 377.71 | 494.43 |
| 4 | 188.85 | 260.99 | 305.57 | 377.71 |
| 5 | 188.85 | 233.44 | 260.99 | 305.57 |
| 6 | 233.44 | 260.99 | 278.02 | 305.57 |
| 7 | 233.44 | 250.47 | 260.99 | 278.02 |
| 8 | 233.44 | 243.96 | 250.47 | 260.99 |
| 9 | 243.96 | 250.47 | 254.49 | 260.99 |
| 10 | 243.96 | 247.98 | 250.47 | 254.49 |
| 11 | 247.98 | 250.47 | 252.00 | 254.49 |
| 12 | 247.98 | 249.52 | 250.47 | 252.00 |
| 13 | 249.52 | 250.47 | 251.05 | 252.00 |
| 14 | 249.52 | 250.10 | 250.47 | 251.05 |
#include "Maximize.h"
/**
* Maximize a "well-behaved" function using the Golden Section algorithm
*/
double maximize(double (*f)(double), double L_0, double U_0, double tol) {
double L, t_L, t_R, U;
// Initialize
L = L_0;
U = U_0;
t_L = L + 0.382 * (U - L);
t_R = L + 0.618 * (U - L);
// Iterate
while ((U - L) > tol) {
if (f(t_L) > f(t_R)) {
// L = L;
U = t_R;
t_R = t_L;
t_L = L + 0.382 * (U - L);
} else {
L = t_L;
// U = U;
t_L = t_R;
t_R = L + 0.618 * (U - L);
}
}
return (U + L) / 2.0;
}