|
Bézier Surfaces in OpenGL
An Introduction |
|
Prof. David Bernstein |
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |
|
Bézier Surfaces in OpenGL
An Introduction |
|
Prof. David Bernstein |
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |
glMapGrid2f()
glEvalMesh2()
An Example
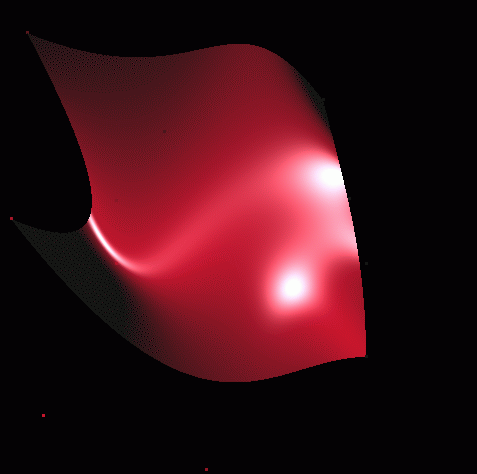
An Example
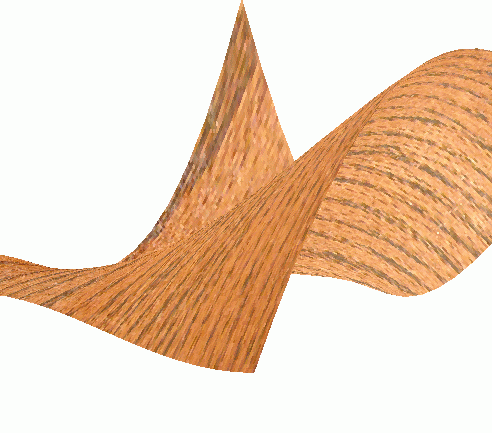
/**
* Initializations
*/
void init() {
glClearColor(1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
glShadeModel(GL_FLAT);
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
// Read the images
GLbyte image[256][256][3];
readRAWImage("oak.raw", image);
// Get "names" for the textures
glGenTextures(1, &textureName);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, textureName);
// Set the parameters
glTexParameterf(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameterf(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameterf(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_NEAREST);
glTexParameterf(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_NEAREST);
// Create the texture object
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, 3, 256, 256, 0, GL_RGB, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE,
image);
// Map the texture
glMap2f(GL_MAP2_TEXTURE_COORD_2, 0, 1, 2, 2, 0, 1, 4, 2,
&textureControlPoints[0][0][0]);
// Create the surface
glMap2f(GL_MAP2_VERTEX_3, 0, 1, 3, uSize, 0, 1, uSize * 3, vSize,
&points[0][0][0]);
glMapGrid2f(gridSize, 0.0, 1.0, gridSize, 0.0, 1.0);
// Enable everything
glEnable(GL_MAP2_TEXTURE_COORD_2);
glEnable(GL_MAP2_VERTEX_3);
}
/**
* The display callback.
*/
void display() {
// Clear the screen
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
// Set the color
glColor3f(1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
// Enable textures
glEnable(GL_TEXTURE_2D);
// Select the texture object
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, textureName);
// Draw the surface
glEvalMesh2(GL_FILL, 0, 20, 0, 20);
// Disable textures (in case you want to render something else)
glDisable(GL_TEXTURE_2D);
// Force the rendering (off-screen)
glFlush();
// Handle the double buffering
glutSwapBuffers();
}