|
Multi-Dimensional Arrays
An Introduction with Examples in Java |
|
Prof. David Bernstein |
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |
|
Multi-Dimensional Arrays
An Introduction with Examples in Java |
|
Prof. David Bernstein |
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |
x1 = 550.75;
x2 = 25.60;
x3 = 347.10;
x4 = 120.45;
x5 = 885.00;
x6 = 10.99;
x7 = 123.45;
x) and refer to
particular elements using the square bracket
operator (e.g., x[i])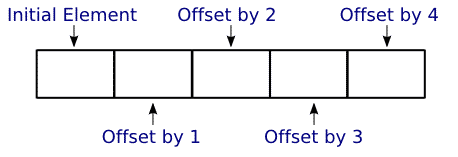
new operator returns a memory address (reference)
which is normally assigned to a variable
// Keep track of the points scored in each game for week 0
int[] pointsScored0 = {58, 60};
// Keep track of the points scored in each game for week 1
int[] pointsScored1 = {72, 48, 61, 44};
// Keep track of the points scored in each game for week 2
int[] pointsScored2 = {60, 63, 51};
Object objects
(which is essentially an array of generic references)
int game, points, week;
int[] temp;
Object[] pointsScored;
pointsScored = new Object[3];
temp = new int[2];
temp[0] = 58;
temp[1] = 60;
pointsScored[0] = temp;
temp = new int[4];
temp[0] = 72;
temp[1] = 48;
temp[2] = 61;
temp[3] = 44;
pointsScored[1] = temp;
temp = new int[3];
temp[0] = 60;
temp[1] = 63;
temp[2] = 51;
pointsScored[2] = temp;
for (week=0; week < pointsScored.length; week++)
{
System.out.printf("\nWeek: %s\n", week);
temp = (int[])pointsScored[week];
for (game=0; game < temp.length; game++)
{
points = temp[game];
System.out.printf(" Game %d: %d\n", game, points);
}
}
Object
array in order to use it[] modifier in the
declaration
[] operator when
accessing
int game, points, week;
int[][] pointsScored; // Note the declaration
// Create a "group" of arrays. There are
// 3 arrays in the "group".
pointsScored = new int[3][];
// Create array zero. There are 2 elements
// in the array.
pointsScored[0] = new int[2];
pointsScored[0][0] = 58; // Note the use of [][]
pointsScored[0][1] = 60; // Note the use of [][]
// Create array one. There are 4 elements
// in the array.
pointsScored[1] = new int[4];
pointsScored[1][0] = 72;
pointsScored[1][1] = 48;
pointsScored[1][2] = 61;
pointsScored[1][3] = 44;
// Create array two. There are 3 elements
// in the array.
pointsScored[2] = new int[3];
pointsScored[2][0] = 60;
pointsScored[2][1] = 63;
pointsScored[2][2] = 51;
// Note the use of pointsScored.length
for (week=0; week < pointsScored.length; week++)
{
System.out.printf("\nWeek: %s\n", week);
// Note the use of pointsScored[].length
// (Watch for ArrayIndexOutOfBounds problems)
for (game=0; game < pointsScored[week].length; game++)
{
System.out.printf(" Game %d: %d\n", game,
pointsScored[week][game]);
}
}
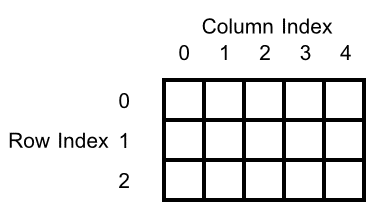
int column, employees, quarters, row;
int[][] sickDays; // Note the declaration
employees = 2;
quarters = 4;
sickDays = new int[employees][quarters];
// Employee 0
sickDays[0][0] = 5; // 5 sick days in quarter 0
sickDays[0][1] = 0; // 0 sick days in quarter 1
sickDays[0][2] = 1; // 1 sick days in quarter 2
sickDays[0][3] = 0; // 0 sick days in quarter 3
// Employee 1
sickDays[1][0] = 2; // 2 sick days in quarter 0
sickDays[1][1] = 1; // 1 sick days in quarter 1
sickDays[1][2] = 4; // 4 sick days in quarter 2
sickDays[1][3] = 3; // 3 sick days in quarter 3
for (row=0; row < employees; row++)
{
for (column=0; column < quarters; column++)
{
System.out.printf("%d\t", sickDays[row][column]);
}
System.out.printf("\n");
}
int column, employees, quarters, row;
// Note the literal
int[][] sickDays = {
{5, 0, 1, 0},
{2, 1, 4, 3},
};
employees = sickDays.length;
quarters = sickDays[0].length;
for (row=0; row < employees; row++)
{
for (column=0; column < quarters; column++)
{
System.out.printf("%d\t", sickDays[row][column]);
}
System.out.printf("\n");
}
int column, row, size;
int[][] table;
size = 10;
table = new int[size][size];
// Generate the entries
for (row=0; row < size; row++)
{
for (column=0; column < size; column++)
{
table[row][column] = row * column;
}
}
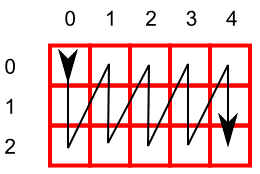
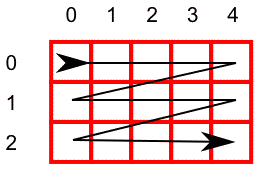
/**
* Print an array of arrays of String objects on System.out.
*
* @param data The data
* @param width The width of each column
*/
public static void print(String[][] data, int width)
{
for (int r = 0; r < data.length; r++) // What is data.length ?
{
for (int c = 0; c < data[r].length; c++) // What is data[r].length?
{
System.out.printf("%"+width+"s", data[r][c]);
}
System.out.printf("\n");
}
}