|
Described Dynamic Visual Content
An Introduction with Examples in Java |
|
Prof. David Bernstein |
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |
|
Described Dynamic Visual Content
An Introduction with Examples in Java |
|
Prof. David Bernstein |
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |
Visualization class, decorating the
Visualization class or specializing
Visualization class
Sprite
package visual.dynamic.described;
import java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D;
import event.MetronomeListener;
import visual.statik.TransformableContent;
/**
* A Sprite is an "actor" on a Stage.
*
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
* @version 1.0
*/
public interface Sprite extends MetronomeListener,
TransformableContent
{
/**
* Returns a high precision bounding box
*
* @return The bounding box
*/
public abstract Rectangle2D getBounds2D();
}
Stage Classpackage visual.dynamic.described;
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.*;
import event.*;
import visual.*;
import visual.statik.sampled.*;
/**
* A Visualization that contains Sprite objects
*
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
* @version 1.0
*
*/
public class Stage extends Visualization
implements MetronomeListener
{
private boolean shouldRestart;
private int timeStep, restartTime, time;
private Metronome metronome;
/**
* Explicit Value Constructor
*
* @param timeStep Amount of time between ticks (in milliseconds)
*/
public Stage(int timeStep)
{
super();
this.timeStep = timeStep;
time = -timeStep;
shouldRestart = false;
restartTime = -1;
metronome = new Metronome(timeStep);
// The first listener is notified last
metronome.addListener(this);
setBackground(Color.WHITE);
}
/**
* Add a Sprite to this Stage
*
* @param sprite The Sprite to add
*/
public void add(Sprite sprite)
{
// Make the Sprite a MetronomeListener
metronome.addListener(sprite);
// Treat the Sprite as a SimpleContent and
// add it to the Visualization
super.add(sprite);
}
/**
* Remove a Sprite from this Stage
*
* @param sprite The Sprite to remove
*/
public void remove(Sprite sprite)
{
metronome.removeListener(sprite);
super.remove(sprite);
}
/**
* Set the background color
*
* Note: If you want to have a background image just
* make it the first SimpleContent
*
* @param background The background color
*/
public void setBackground(Color background)
{
Iterator<VisualizationView> i;
VisualizationView view;
i = getViews();
while (i.hasNext())
{
view = i.next();
view.setBackground(background);
}
}
/**
* Set the time at which the Stage should restart
*
* @param restartTime In milliseconds (negative to not restart)
*/
public void setRestartTime(int restartTime)
{
if (restartTime < 0)
{
this.restartTime = -1;
shouldRestart = false;
}
else
{
this.restartTime = restartTime;
shouldRestart = true;
}
}
/**
* Start the Stage
*/
public void start()
{
metronome.start();
}
/**
* Stop the Stage
*/
public void stop()
{
metronome.stop();
}
}
/**
* Handle "tick" events (required by MetronomeTickListener)>
*
* @param time The time of the "tick"
*/
public void handleTick(int time)
{
if ((shouldRestart) && (time > restartTime))
{
metronome.setTime(-timeStep);
}
repaint();
}
SimpleContent with a particular
AbstractSprite at different points in time
AbstractSprite Classpackage visual.dynamic.described;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.geom.*;
import java.util.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import event.*;
import visual.statik.TransformableContent;
/**
* A Sprite is an "actor" on a Stage.
*
* In essence, a Sprite decorates a TransformableContent object,
* providing it with additional capabilities.
*
* Note:
*
* We don't immediately delegate since the content and the
* location/rotation/scale may change at any time and in any
* order. Instead, we set the location/rotation/scale before
* rendering.
*
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
* @version 1.0
*/
public abstract class AbstractSprite
implements MetronomeListener,
Sprite,
TransformableContent
{
protected boolean rotationPoint, visible;
protected double angle, rotationX, rotationY;
protected double scaleX, scaleY, x, y;
/**
* Default Constructor
*/
public AbstractSprite()
{
super();
x = 0.0;
y = 0.0;
angle = 0.0;
scaleX = 1.0;
scaleY = 1.0;
rotationPoint = false;
rotationX = 0.0;
rotationY = 0.0;
}
/**
* Returns a high precision bounding box of the Content
* either before or after it is transformed
*
* @param ofTransformed true to get the BB of the transformed content
* @return The bounding box
*/
public Rectangle2D getBounds2D(boolean ofTransformed)
{
return getContent().getBounds2D(true);
}
/**
* Returns a high precision bounding box
*
* @return The bounding box
*/
public Rectangle2D getBounds2D()
{
return getBounds2D(true);
}
/**
* Gets the (current) visual content for this Sprite
*
* This method is called by various setters and the render()
* method.
*/
protected abstract TransformableContent getContent();
/**
* Handle a tick event
* (required by MetronomeListener)
*
* @param time The current time (in milliseconds)
*/
public abstract void handleTick(int time);
/**
* Initialize state variables
*/
protected void reinitialize()
{
setScale(1.0);
setRotation(0.0);
setLocation(0.0, 0.0);
setVisible(false);
}
/**
* Set the location (on the Stage) of the Sprite
*
* @param x The horizontal location
* @param y The vertical location
*/
public void setLocation(double x, double y)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
/**
* Set the rotation angle and point to rotate around
*
* @param r The new rotation angle
* @param x The x-coordinate of the point to rotate around
* @param y The y-coordinate of the point to rotate around
*/
public void setRotation(double r, double x, double y)
{
rotationPoint = true;
this.angle = r;
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
/**
* Set the rotation angle (the Sprite will rotate
* around its midpoint)
*
* @param r The new rotation angle
*/
public void setRotation(double r)
{
rotationPoint = false;
this.angle = r;
}
/**
* Set the scaling (enlargement, reduction) of the Sprite
*
* @param sx The scale in the x-dimension
* @param sy The scale in the y-dimension
*/
public void setScale(double sx, double sy)
{
scaleX = sx;
scaleY = sy;
}
/**
* Set the scaling (enlargement, reduction) of the Sprite
*
* @param s The new scale
*/
public void setScale(double s)
{
setScale(s, s);
}
/**
* Set the visibility of this Sprite
*
* @param v true for visible, false for invisible
*/
public void setVisible(boolean v)
{
visible = v;
}
}
/**
* Render this Sprite
*
* @param g The rendering engine to use
*/
public void render(Graphics g)
{
double rx, ry;
Rectangle2D bounds;
TransformableContent tc;
if (visible)
{
tc = getContent();
if (tc != null)
{
// Find the point to rotate around
if (rotationPoint)
{
rx = rotationX;
ry = rotationY;
}
else
{
bounds = tc.getBounds2D(false);
rx = bounds.getWidth()/2.0;
ry = bounds.getHeight()/2.0;
}
// Transform
tc.setLocation(x, y);
tc.setRotation(angle, rx, ry);
tc.setScale(scaleX, scaleY);
// Render
tc.render(g);
}
}
}
FloatingSprite
package visual.dynamic.described;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.geom.*;
import java.util.*;
import visual.statik.TransformableContent;
/**
* A simple Sprite
*
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
* @version 1.0
*
*/
public class FloatingSprite extends AbstractSprite
{
private double maxX, maxY, x, y;
private Random rng;
private TransformableContent content;
/**
* Explicit Value Constructor
*
* @param content The static visual content
* @param width The width of the Stage
* @param height The height of the Stage
*/
public FloatingSprite(TransformableContent content,
double width, double height)
{
super();
this.content = content;
maxX = width;
maxY = height;
rng = new Random();
x = rng.nextDouble()*maxX;
y = 0.0;
setLocation(x, y);
setVisible(true);
}
}
/**
* Get the visual content associated with this Sprite
* (required by Sprite)
*/
public TransformableContent getContent()
{
return content;
}
/**
* Handle a tick event (required by MetronomeListener)
*
* @param time The current time (in milliseconds)
*/
public void handleTick(int time)
{
double n;
n = rng.nextDouble();
if (n < 0.80) y += 2.0;
else if (n > 0.90) y -= 1.0;
n = rng.nextDouble();
if (n < 0.20) x -= 1.0;
else if (n > 0.80) x += 1.0;
// Check if at the bottom
if (y > maxY)
{
y = 0.0;
x = rng.nextDouble()*maxX;
}
setLocation(x, y);
}
FloatingSprite
ContentFactory contentFactory;
FloatingSprite sprite;
int height, width;
JPanel contentPane;
Stage stage;
TransformableContent content;
VisualizationView stageView;
width = 640;
height = 480;
// The Stage
stage = new Stage(50);
stage.setBackground(new Color(255, 255, 255));
stageView = stage.getView();
stageView.setBounds(0,0,width,height);
// The Sprite
contentFactory = new ContentFactory();
content = contentFactory.createContent(
"/visual/dynamic/described/snowflake.gif",
4, false);
sprite = new FloatingSprite(content, width, height);
stage.add(sprite);
// The content pane
contentPane = (JPanel)rootPaneContainer.getContentPane();
contentPane.add(stageView);
// Start the dynamics
stage.start();
handleTick() method
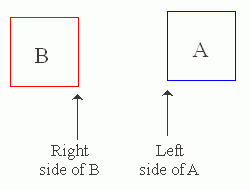
Rectangular Sprites
Non-Rectangular Sprites
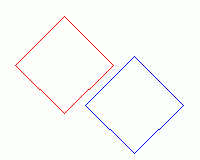
Non-Convex Sprites
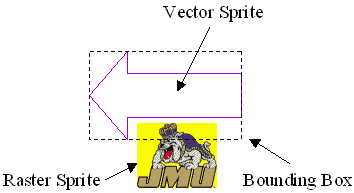
Using Bounding Boxes
Sprite Class
/**
* Does the bounding box of this Sprite intersect the
* bounding box of the given Sprite? (given their current state)
*
* @param s The other Sprite
* @return true if the two intersect
*/
public boolean intersects(Sprite s)
{
boolean retval;
double maxx, maxy, minx, miny;
double maxxO, maxyO, minxO, minyO;
Rectangle2D r;
retval = true;
r = getBounds2D();
minx = r.getX();
miny = r.getY();
maxx = minx + r.getWidth();
maxy = miny + r.getHeight();
r = s.getBounds2D();
minxO = r.getX();
minyO = r.getY();
maxxO = minxO + r.getWidth();
maxyO = minyO + r.getHeight();
if ( (maxx < minxO) || (minx > maxxO) ||
(maxy < minyO) || (miny > maxyO) ) retval = false;
return retval;
}
package visual.dynamic.described;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.geom.*;
import java.util.*;
import visual.statik.TransformableContent;
/**
* An abstract rule-based Sprite
*
* Note: Concrete descendents must implement the
* handleTick() method
*
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
* @version 1.0
*
*/
public abstract class RuleBasedSprite extends AbstractSprite
{
protected ArrayList<Sprite> protagonists;
protected TransformableContent content;
/**
* Explicit Value Constructor
*
* @param content The static visual content
*/
public RuleBasedSprite(TransformableContent content)
{
super();
protagonists = new ArrayList<Sprite>();
this.content = content;
setVisible(true);
}
/**
* Add a "protagonist" Sprite to this Sprite
*
* @param protagonist The "protagonist" Sprite to add
*/
public void addProtagonist(Sprite protagonist)
{
protagonists.add(protagonist);
}
/**
* Get the visual content associated with this Sprite
* (required by Sprite)
*/
public TransformableContent getContent()
{
return content;
}
/**
* Handle a tick event (required by MetronomeListener)
*
* @param time The current time (in milliseconds)
*/
public abstract void handleTick(int time);
/**
* Remove a "protagonist" Sprite from the collection of
* "protagonists" this Sprite is concerned with
*
* @param protagonist The "protagonist" Sprite to remove
*/
public void removeProtagonist(Sprite protagonist)
{
protagonists.remove(protagonist);
}
}
package visual.dynamic.described;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.image.RasterFormatException;
import java.awt.geom.*;
import java.util.Random;
import visual.statik.TransformableContent;
/**
* A Fish that "swims" around and avoids its "protagonists"
* (in a simple way)
*
* Note: This is a simple rule-based Sprite.
* Hence, it has rules in handleTick().
*
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
* @version 1.0
*
*/
public class Fish extends RuleBasedSprite
{
protected double maxX, maxY, speed, x, y;
protected Random rng;
/**
* Explicit Value Constructor
*
* @param content The static visual content
* @param width The width of the Stage
* @param height The height of the Stage
*/
public Fish(TransformableContent content,
double width, double height)
{
super(content);
maxX = width;
maxY = height;
rng = new Random();
x = rng.nextDouble()*maxX;
y = rng.nextInt()*maxY;
speed = 3.0;
}
/**
* Handle a tick event (generated by the Stage)
*
* @param time The current time (which is not used)
*/
public void handleTick(int time)
{
Sprite shark;
shark = null;
if (protagonists.size() > 0) shark = protagonists.get(0);
if ((shark != null) && (intersects(shark)))
{
speed = 20;
}
updateLocation(-50., 3.);
}
/**
* Update the location
*
* @param initialLocation The left-most location
* @param initialSpeed The speed to start at
*/
protected void updateLocation(double initialLocation,
double initialSpeed)
{
x += speed;
if (x > (int)maxX)
{
x = initialLocation;
y = rng.nextDouble()*maxX;
speed = initialSpeed;
}
// Set the location
setLocation(x, y);
}
}
package visual.dynamic.described;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.font.*;
import java.awt.geom.*;
import java.awt.image.RasterFormatException;
import java.util.Random;
import visual.statik.TransformableContent;
/**
* A Shark that "swims" around
*
* Note: This is a simple rule-based Sprite.
* Hence, it has rules in handleTick().
*
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
* @version 1.0
*/
public class Shark extends Fish
{
/**
* Explicit Value Constructor
*
* @param content The static visual content
* @param width The width of the Stage
* @param height The height of the Stage
*/
public Shark(TransformableContent content,
double width, double height)
{
super(content, width, height);
speed = 8.0;
}
/**
* Handle a tick event (generated by the Stage)
*
* @param time The current time (which is not used)
*/
public void handleTick(int time)
{
updateLocation(-320.0, 6.0);
}
}
package visual.dynamic.described;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.geom.*;
import java.awt.image.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import app.*;
import visual.VisualizationView;
import visual.dynamic.described.Fish;
import visual.dynamic.described.Shark;
import visual.dynamic.described.Stage;
import visual.statik.sampled.ImageFactory;
import visual.statik.sampled.Content;
import visual.statik.sampled.ContentFactory;
/**
* An example of described dynamic visual content that uses:
*
* Several RuleBasedSprite objects
* Interaction
*
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
* @version 1.0
*
*/
public class FishTankApp
extends AbstractMultimediaApp
{
/**
* The entry point
*/
public void init()
{
BufferedImage image;
Content content;
ContentFactory factory;
Fish fish;
ImageFactory imageFactory;
int height, width;
JPanel contentPane;
Shark shark;
Stage stage;
VisualizationView stageView;
width = 640;
height = 480;
factory = new ContentFactory();
imageFactory = new ImageFactory();
// The Stage
stage = new Stage(50);
stage.setBackground(Color.blue);
content = factory.createContent(
"/visual/dynamic/described/ocean.gif", 3, false);
stage.add(content);
stageView = stage.getView();
stageView.setBounds(0,0,width,height);
// The Shark
content = factory.createContent(
"/visual/dynamic/described/shark.gif", 4, false);
shark = new Shark(content, width, height);
stage.add(shark);
// The school of Fish
// (Using the same BufferedImage object for all Fish)
image = imageFactory.createBufferedImage(
"/visual/dynamic/described/fish.gif", 4);
for (int i=0; i<6; i++)
{
content = factory.createContent(image, false);
fish = new Fish(content, width, height);
fish.addProtagonist(shark);
stage.add(fish);
}
// The content pane
contentPane = (JPanel)rootPaneContainer.getContentPane();
contentPane.add(stageView);
stage.start();
}
}
Sprite a
KeyListener, MouseListener or
MouseMotionListener
Visualization Class
/**
* Add a KeyListener
*
* @param kl The listener to add
*/
public void addKeyListener(KeyListener kl)
{
Iterator<VisualizationView> i;
VisualizationView view;
i = getViews();
while (i.hasNext())
{
view = i.next();
view.addKeyListener(kl);
}
}
/**
* Add a MouseListener
*
* @param ml The listener to add
*/
public void addMouseListener(MouseListener ml)
{
Iterator<VisualizationView> i;
VisualizationView view;
i = getViews();
while (i.hasNext())
{
view = i.next();
view.addMouseListener(ml);
}
}
/**
* Add a MouseMotionListener
*
* @param mml The listener to add
*/
public void addMouseMotionListener(
MouseMotionListener mml)
{
Iterator<VisualizationView> i;
VisualizationView view;
i = getViews();
while (i.hasNext())
{
view = i.next();
view.addMouseMotionListener(mml);
}
}
package visual.dynamic.described;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.awt.geom.*;
import visual.statik.TransformableContent;
/**
* The Cupola in the Balloon game.
*
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
* @version 1.0
*/
public class Cupola extends RuleBasedSprite
implements MouseMotionListener
{
private double left, top;
/**
* Explicit Value Constructor
*
* @param content The static visual content
* @param stageWidth The width of the Stage
* @param stageHeight The height of the Stage
*/
public Cupola(TransformableContent content,
double stageWidth, double stageHeight)
{
super(content);
Rectangle2D bounds;
bounds = content.getBounds2D(false);
top = (stageHeight - bounds.getHeight());
left = (stageWidth - bounds.getWidth())/2.0;
setLocation(left, top);
}
}
/**
* Handle a mouseDragged message
* (required by MouseMotionListener)
*
* @param evt The MouseEvent that generated the message
*/
public void mouseDragged(MouseEvent evt)
{
mouseMoved(evt);
}
/**
* Handle a mouseMoved message
* (required by MouseMotionListener)
*
* @param evt The MouseEvent that generated the message
*/
public void mouseMoved(MouseEvent evt)
{
this.left = (double)evt.getX();
}
/**
* Handle a tick event (generated by the Stage)
*
* @param time The current time (which is not used)
*/
public void handleTick(int time)
{
setLocation(left, top);
}
package visual.dynamic.described;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.geom.*;
import java.util.Random;
import visual.statik.TransformableContent;
/**
* A Balloon that drops to the ground
*
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
* @version 1.0
*/
public class Balloon extends RuleBasedSprite
{
private double left, speed, top;
private int maxY, maxX, minY;
private static Random rng = new Random();
/**
* Explicit Value Constructor
*
* @param content The static content for the balloon
* @param stageWidth The width of the Stage
* @param stageHeight The height of the Stage
*/
public Balloon(TransformableContent content,
double stageWidth, double stageHeight)
{
super(content);
Rectangle2D bounds;
bounds = content.getBounds2D(false);
maxX = (int)(stageWidth - bounds.getWidth());
maxY = (int)(stageHeight);
minY = (int)(-bounds.getHeight());
left = rng.nextInt(maxX);
top = minY;
speed = 1 + rng.nextInt(10);
}
/**
* Handle a tick event (generated by the Stage)
*
* @param time The current time (which is not used)
*/
public void handleTick(int time)
{
Sprite cupola;
// Check for an intersection
cupola = null;
if (protagonists.size() > 0) cupola = protagonists.get(0);
if ((cupola != null) && (intersects(cupola)))
{
speed = 0;
setVisible(false);
}
// Update the location
top += speed;
if (top > maxY)
{
left = rng.nextInt(maxX);
top = minY;
speed = rng.nextInt(10);
}
// Set the location
setLocation(left, top);
}
}
TransformableContent objects themselves
TweeningSprite Classpackage visual.dynamic.described;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.geom.*;
import java.util.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* A TweeningSprite is a Sprite that contains "key times" and the ability
* to generate "in between times"
*
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
* @version 1.0
*/
public abstract class TweeningSprite extends AbstractSprite
{
private double frac;
private int currentIndex, endState, lastTime;
private int localTime, nextIndex, nextKT;
protected Vector<Integer> keyTimes;
protected Vector<Point2D> locations;
protected Vector<Double> rotations, scalings;
public static final int REMAIN = 0;
public static final int REMOVE = 1;
public static final int REPEAT = 2;
/**
* Default Constructor
*/
public TweeningSprite()
{
super();
keyTimes = new Vector<Integer>();
locations = new Vector<Point2D>();
rotations = new Vector<Double>();
scalings = new Vector<Double>();
localTime = 0;
lastTime = -1;
initialize();
}
}
/**
* Add a key time
*
* @param keyTime The time
* @param location The location of the sprite at this time
* @param rotation The rotation of the sprite (null to align with path)
* @param scaling The scaling of the sprite at this time
*
* @return The index of this key time (or -1 if the key time exists)
*/
protected int addKeyTime(int keyTime, Point2D location,
Double rotation, Double scaling)
{
boolean keepLooking;
int existingKT, i, index;
existingKT = -1;
keepLooking = true;
i = 0;
while ((i < keyTimes.size()) && keepLooking)
{
existingKT = ((Integer)keyTimes.get(i)).intValue();
if (existingKT >= keyTime) keepLooking = false;
else i++;
}
if ((existingKT == i) && !keepLooking) // Duplicate
{
i = -1;
}
else
{
keyTimes.insertElementAt(new Integer(keyTime), i);
locations.insertElementAt(location, i);
rotations.insertElementAt(rotation, i);
scalings.insertElementAt(scaling, i);
}
return i;
}
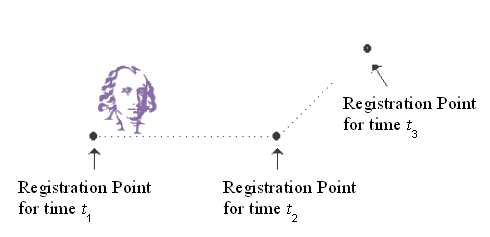
TweeningSprite Class
/**
* Determine the current 'tweened location
*
* @param currentIndex The index of the current key time
* @param nextIndex The index of the next key time
* @param frac The interpolation fraction
*/
protected void tweenLocation(int currentIndex, int nextIndex,
double frac)
{
double x, y;
Point2D currentKTLocation, nextKTLocation;
currentKTLocation = locations.get(currentIndex);
nextKTLocation = locations.get(nextIndex);
x = currentKTLocation.getX() +
frac*(nextKTLocation.getX()- currentKTLocation.getX());
y = currentKTLocation.getY() +
frac*(nextKTLocation.getY() - currentKTLocation.getY());
setLocation(x, y);
}
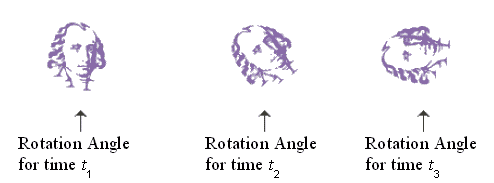
TweeningSprite Class
/**
* Determine the current 'tweened rotation
*
* @param currentIndex The index of the current key time
* @param nextIndex The index of the next key time
* @param frac The interpolation fraction
*/
protected void tweenRotation(int currentIndex, int nextIndex,
double frac)
{
double currentKTRotation, nextKTRotation, r;
Double rotation;
Point2D currentKTLocation, nextKTLocation;
rotation = rotations.get(currentIndex);
if (rotation == null) // aligned with the line segment
{
currentKTLocation = locations.get(currentIndex);
nextKTLocation = locations.get(nextIndex);
r=Math.atan((nextKTLocation.getY()-currentKTLocation.getY())/
(nextKTLocation.getX()-currentKTLocation.getX()) );
}
else // pure rotation tweening
{
currentKTRotation = rotation.doubleValue();
rotation = rotations.get(nextIndex);
if (rotation == null)
{
nextKTRotation = currentKTRotation;
}
else
{
nextKTRotation = rotation.doubleValue();
}
r = currentKTRotation + frac*(nextKTRotation-currentKTRotation);
}
setRotation(r);
}
package visual.dynamic.described;
import java.awt.geom.*;
import java.awt.image.*;
import visual.statik.sampled.*;
/**
* An Airplane
*
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
* @version 1.0
*
*/
public class Airplane extends SampledSprite
{
/**
* Default Constructor
*
*/
public Airplane()
{
super();
Content content;
ContentFactory factory;
factory = new ContentFactory();
content = factory.createContent(
"/visual/dynamic/described/airplane.gif", 4);
addKeyTime( 500, 0.0, 350.0, -0.75, 1.0, content);
addKeyTime( 2000, 100.0, 200.0, -0.30, 1.0, null);
addKeyTime( 4000, 200.0, 50.0, 0.00, 1.0, null);
addKeyTime( 6000, 300.0, 50.0, 0.20, 1.0, null);
addKeyTime( 8000, 400.0, 200.0, 0.00, 1.0, null);
addKeyTime( 8500, 500.0, 200.0, 0.00, 1.0, null);
setEndState(REMOVE);
}
/**
* Add a key frame
*/
private void addKeyTime(int time, double x, double y,
double r, double s, Content c)
{
addKeyTime(time, new Point2D.Double(x, y), new Double(r),
new Double(s), c);
}
}
package visual.dynamic.described;
import java.awt.geom.Point2D;
import visual.statik.described.*;
/**
* A Buzzy moving on Mars
*
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
* @version 1.0
*
*/
public class BuzzyOnMars extends DescribedSprite
{
/**
* Default Constructor
*/
public BuzzyOnMars()
{
super();
BuzzyStanding buzzy;
buzzy = new BuzzyStanding();
addKeyTime( 500, 0.0, 380.0, 0.00, 1.0, buzzy);
addKeyTime( 2000, 180.0, 380.0, 0.00, 1.0, null);
addKeyTime( 4000, 180.0, 75.0, 0.20, 1.0, null);
addKeyTime( 6000, 640.0, 20.0, 6.48, 1.0, null);
setEndState(REMOVE);
}
/**
* Add a key time
*
* @param time The key time
* @param x The x position
* @param y The y position
* @param r The rotation angle
* @param r The scaling
* @param c The Content
*/
private void addKeyTime(int time, double x, double y,
double r, double s, AggregateContent c)
{
addKeyTime(time, new Point2D.Double(x, y), new Double(r),
new Double(s), c);
}
}
package visual.dynamic.described;
import java.awt.geom.Point2D;
import visual.statik.sampled.*;
/**
* The Bus in the Transit Information System
*
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
* @version 1.0
*
*/
public class BusOnRoute extends SampledSprite
{
/**
* Default Constructor
*
* @param fn The file containing the bitmap
*/
public BusOnRoute()
{
super();
Content content;
ContentFactory factory;
factory = new ContentFactory();
content = factory.createContent(
"/visual/dynamic/described/bus.gif");
addKeyTime( 0, 164, 210, content);
addKeyTime( 1, 310, 255, null);
addKeyTime( 2, 314, 234, null);
addKeyTime( 3, 401, 231, null);
addKeyTime( 4, 419, 269, null);
addKeyTime( 5, 353, 340, null);
addKeyTime( 6, 430, 367, null);
addKeyTime( 7, 420, 418, null);
addKeyTime( 8, 450, 421, null);
addKeyTime( 9, 454, 386, null);
addKeyTime(10, 512, 393, null);
addKeyTime(11, 487, 338, null);
addKeyTime(12, 554, 323, null);
addKeyTime(13, 500, 238, null);
addKeyTime(14, 577, 206, null);
addKeyTime(15, 632, 155, null);
addKeyTime(16, 480, 151, null);
addKeyTime(19, 301, 88, null);
addKeyTime(21, 233, 149, null);
addKeyTime(22, 147, 181, null);
addKeyTime(30, 164, 210, null);
setEndState(REMOVE);
}
/**
* Add a key time
*
* @param time The key time
* @param x The x position
* @param y The y position
* @param content The Content to use
*/
private void addKeyTime(int time, int x, int y,
Content content)
{
addKeyTime(time*1000, new Point2D.Double((double)x, (double)y),
null,
new Double(1.0), content);
}
}
package visual.statik.sampled;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.image.*;
import java.util.Iterator;
/**
* A simple collection of Content objects
*
* This class is less flexible than the CompositeContent class
* but is simpler for some purposes.
*
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
* @version 1.0
*/
public class AggregateContent
extends visual.statik.AbstractAggregateContent<Content>
implements TransformableContent
{
/**
* Default Constructor
*/
public AggregateContent()
{
super();
}
/**
* Set the BufferedImageOp to use when transforming
* the Image
*
* @param op The BufferedImageOp
*/
public void setBufferedImageOp(BufferedImageOp op)
{
Iterator<Content> i;
i = iterator();
while (i.hasNext())
{
i.next().setBufferedImageOp(op);
}
}
/**
* Set the transparency/Composite to use
* for the LAST Content object
*
* @param c The Composite
*/
public void setComposite(Composite c)
{
Content content;
content = components.getLast();
content.setComposite(c);
}
}
package visual.dynamic.described;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.geom.*;
import java.awt.image.*;
import java.util.Vector;
import visual.statik.sampled.AggregateContent;
import visual.statik.sampled.Content;
import visual.statik.sampled.TransformableContent;
/**
* A TweeningSprite that uses sampled visual content
*
* Note: This class uses a Vector of Content
* objects rather than a CompositeContent object for
* efficiency reasons.
*
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
* @version 1.0
*/
public class SampledSprite extends TweeningSprite
{
private AggregateContent tweened;
private Vector<Content> content;
/**
* Default Constructor
*/
public SampledSprite()
{
super();
content = new Vector<Content>();
}
/**
* Add a key time
*
* Note: This method does not ensure that the first key
* frame actually contains an image.
*
* @param keyTime The time
* @param location The location of the sprite at this time
* @param rotation The rotation of the sprite (null to align with path)
* @param scaling The scaling of the sprite at this time
* @param c The Content to use (or null to use previous)
*/
public void addKeyTime(int keyTime, Point2D location,
Double rotation, Double scaling,
Content c)
{
int index;
index = super.addKeyTime(keyTime, location, rotation, scaling);
if (index >= 0)
{
// If c is null then re-use the last Content
if (c==null) c = content.get(index-1);
content.insertElementAt(c, index);
}
}
/**
* Get the visual content
* (based on this Sprite's current state)
*/
protected visual.statik.TransformableContent getContent()
{
AggregateContent aggregate;
Content currentContent, nextContent;
float alpha;
int current, next;
visual.statik.TransformableContent result;
result = null;
current = getKeyTimeIndex();
next = getNextKeyTimeIndex();
if (visible && (current >= 0))
{
currentContent = content.get(current);
nextContent = content.get(next);
if ((nextContent != null) &&
(currentContent != nextContent))
{
aggregate = new AggregateContent();
aggregate.add(currentContent);
aggregate.add(nextContent);
// Setup alpha blending
alpha = (float)getInterpolationFraction();
aggregate.setComposite(
AlphaComposite.getInstance(
AlphaComposite.SRC_OVER,
alpha));
result = aggregate;
}
else
{
result = currentContent;
}
}
return result;
}
}
package visual.dynamic.described;
import java.awt.geom.Point2D;
import visual.statik.sampled.*;
/**
* An animated crystal ball
*
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
* @version 1.0
*
*/
public class CrystalBall extends SampledSprite
{
/**
* Default Constructor
*
*/
public CrystalBall()
{
super();
Content content;
ContentFactory factory;
factory = new ContentFactory();
content = factory.createContent(
"/visual/dynamic/described/crystalball01.gif");
addKeyTime( 500, 0.0, 350.0, -0.75, content);
addKeyTime( 4000, 100.0, 200.0, -0.30, null);
content = factory.createContent(
"/visual/dynamic/described/crystalball02.gif");
addKeyTime( 7500, 200.0, 50.0, 0.00, content);
setEndState(REMAIN);
}
/**
* Add a key time
*
* @param time The key time
* @param x The x position
* @param y The y position
* @param r The rotation angle
* @param content The static visual content
*/
private void addKeyTime(int time, double x, double y,
double r, Content content)
{
addKeyTime(time, new Point2D.Double(x, y), new Double(r),
new Double(1.0), content);
}
}
package visual.dynamic.described;
import java.awt.geom.Point2D;
import visual.statik.sampled.*;
/**
* A morphing Professor
*
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
* @version 1.0
*
*/
public class Professor extends SampledSprite
{
/**
* Default Constructor
*
*/
public Professor()
{
super();
Content content;
ContentFactory factory;
factory = new ContentFactory();
content = factory.createContent(
"/visual/dynamic/described/bernstein.gif", 4);
addKeyTime( 0, 0.0, 0.0, content);
content = factory.createContent(
"/visual/dynamic/described/abzug.gif", 4);
addKeyTime(10000, 0.0, 0.0, content);
setEndState(REMAIN);
}
/**
* Add a key time
*
* @param time The key time
* @param x The x position
* @param y The y position
* @param r The rotation angle
* @param image The image
*/
private void addKeyTime(int time, double x, double y,
Content content)
{
addKeyTime(time, new Point2D.Double(x, y), new Double(0.0),
new Double(1.0), content);
}
}
Shape Tweening
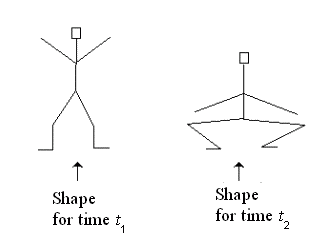
java/awt/geom/PathIterator

/**
* Get a PathIterator
*
* @param transformed true to get the transformed version
* @return The PathIterator
*/
public PathIterator getPathIterator(boolean transformed)
{
if (transformed)
return transformedShape.getPathIterator(IDENTITY);
else
return originalShape.getPathIterator(IDENTITY);
}
described.AggregateContent
package visual.statik.described;
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.Iterator;
/**
* A simple collection of Content objects
*
* This class is less flexible than the CompositeContent class
* but is simpler for some purposes.
*
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
* @version 1.0
*/
public class AggregateContent
extends visual.statik.AbstractAggregateContent<Content>
implements TransformableContent
{
/**
* Default Constructor
*/
public AggregateContent()
{
super();
}
/**
* Set the Color to use for stroking
*
* @param color The Color to use (or null to prevent stroking)
*/
public void setColor(Color color)
{
Iterator<Content> i;
i = iterator();
while (i.hasNext())
{
i.next().setColor(color);
}
}
/**
* Set the Paint to use for filling
*
* @param paint The Paint to use (or null to prevent filling)
*/
public void setPaint(Paint paint)
{
Iterator<Content> i;
i = iterator();
while (i.hasNext())
{
i.next().setPaint(paint);
}
}
/**
* Set the Stroke to use
*
* @param stroke The Stroke to use (or null to use the default)
*/
public void setStroke(Stroke stroke)
{
Iterator<Content> i;
i = iterator();
while (i.hasNext())
{
i.next().setStroke(stroke);
}
}
}
DescribedSprite
package visual.dynamic.described;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.geom.*;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Vector;
import visual.statik.described.*;
/**
* A TweeningSprite that uses described visual content
*
* Note: This class uses a Vector of AggregateContent
* objects rather than CompositeContent objects for
* simplicity.
*
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
* @version 1.0
*/
public class DescribedSprite extends TweeningSprite
{
private AggregateContent tweened;
private Vector<AggregateContent> content;
/**
* Default Constructor
*/
public DescribedSprite()
{
content = new Vector<AggregateContent>();
tweened = new AggregateContent();
}
/**
* Add a key time
*
* Note: This method does not ensure that the first key
* time actually contains static visual content
*
* @param keyTime The time
* @param location The location of the sprite at this time
* @param rotation The rotation of the sprite (null to align with path)
* @param scaling The scaling of the sprite at this time
* @param ctc The Content to use (or null to use previous Content)
*/
public void addKeyTime(int keyTime, Point2D location,
Double rotation, Double scaling,
AggregateContent ctc)
{
int index;
index = super.addKeyTime(keyTime, location, rotation, scaling);
if (index >= 0)
{
// If ctc is null then re-use the last CompositeContent
if (ctc == null) ctc = content.get(index-1);
content.insertElementAt(ctc, index);
}
}
/**
* Get the visual content
* associated with this Sprite
*
* Note that the visual content created depends on the
* current state of this Sprite
*
* @param at The AffineTransform to use
* @return The transformed content
*/
public visual.statik.TransformableContent getContent()
{
int current, next;
AggregateContent currentCTC, nextCTC, result;
current = getKeyTimeIndex();
next = getNextKeyTimeIndex();
result = null;
if (current >= 0)
{
currentCTC = content.get(current);
nextCTC = content.get(next);
//result = currentCTC.clone();
result = currentCTC;
if (currentCTC != nextCTC)
{
tweenShape(currentCTC, nextCTC, getInterpolationFraction());
result = tweened;
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* Determine the current 'tweened shape
*
* @param a The first shape
* @param b The second shape
* @param frac The interpolation fraction
*/
protected void tweenShape(AggregateContent a,
AggregateContent b,
double frac)
{
Color color;
float[] coords, coordsA, coordsB;
GeneralPath gp;
int seg;
Iterator<Content> iterA, iterB;
PathIterator piA, piB;
Paint paint;
Content shapeA, shapeB;
Stroke stroke;
//tweened.clear();
tweened = new AggregateContent();
coordsA = new float[6];
coordsB = new float[6];
coords = new float[6];
iterA = a.iterator();
iterB = b.iterator();
// Loop over all of the TransformableContent objects
// in the CompositeTransformableContent
while (iterA.hasNext())
{
shapeA = iterA.next();
if (iterB.hasNext()) shapeB = iterB.next();
else shapeB = shapeA;
piA = shapeA.getPathIterator(false);
piB = shapeB.getPathIterator(false);
gp = new GeneralPath();
gp.setWindingRule(piA.getWindingRule());
// Loop over all of the segments in the
// TransformableContent object
while (!piA.isDone())
{
seg = piA.currentSegment(coordsA);
if (piB.isDone()) // Use the coordinates of the first shape
{
for (int i=0; i < coordsA.length; i++)
coords[i] = coordsA[i];
}
else // Interpolate the coordinates
{
piB.currentSegment(coordsB);
for (int i=0; i < coordsA.length; i++)
{
coords[i] = coordsA[i] +
(float)frac*(coordsB[i] - coordsA[i]);
}
}
// Add to the General Path object
if (seg == PathIterator.SEG_MOVETO)
{
gp.moveTo(coords[0], coords[1]);
}
else if (seg == PathIterator.SEG_LINETO)
{
gp.lineTo(coords[0], coords[1]);
}
else if (seg == PathIterator.SEG_QUADTO)
{
gp.quadTo(coords[0], coords[1], coords[2], coords[3]);
}
else if (seg == PathIterator.SEG_CUBICTO)
{
gp.curveTo(coords[0], coords[1],
coords[2], coords[3],
coords[4], coords[5]);
}
else if (seg == PathIterator.SEG_CLOSE)
{
gp.closePath();
}
piA.next();
piB.next();
}
paint = shapeA.getPaint();
color = shapeA.getColor(); // This could also be tweened
stroke = shapeA.getStroke();
tweened.add(new Content(gp, color, paint, stroke));
}
}
}
package visual.dynamic.described;
import java.awt.geom.Point2D;
import visual.statik.described.*;
/**
* A Buzzy jumping
*
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
* @version 1.0
*
*/
public class BuzzyJumping extends DescribedSprite
{
/**
* Default Constructor
*
*/
public BuzzyJumping()
{
super();
addKeyTime( 1000, 0.0, 355.0, 0.00, new BuzzyStanding());
addKeyTime( 1500, 0.0, 355.0, 0.00, new BuzzyCrouching());
addKeyTime( 2000, 0.0, 355.0, 0.00, new BuzzyLeaningForward());
addKeyTime( 4000, 180.0, 75.0, 0.00, new BuzzyLeaningForward());
addKeyTime( 6000, 540.0, 355.0, 0.00, new BuzzyCrouching());
addKeyTime( 6500, 540.0, 355.0, 0.00, new BuzzyStanding());
setEndState(REMAIN);
}
/**
* Add a key time
*
* @param time The key time
* @param x The x position
* @param y The y position
* @param r The rotation angle
* @param content The static visual content
*/
private void addKeyTime(int time, double x, double y,
double r, AggregateContent content)
{
addKeyTime(time, new Point2D.Double(x, y), new Double(r),
new Double(1.0), content);
}
}
DescribedSprite
package visual.dynamic.described;
import java.awt.geom.Point2D;
import visual.statik.described.*;
/**
* A Buzzy jumping
*
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
* @version 1.0
*
*/
public class BuzzyJumping extends DescribedSprite
{
/**
* Default Constructor
*
*/
public BuzzyJumping()
{
super();
addKeyTime( 1000, 0.0, 355.0, 0.00, new BuzzyStanding());
addKeyTime( 1500, 0.0, 355.0, 0.00, new BuzzyCrouching());
addKeyTime( 2000, 0.0, 355.0, 0.00, new BuzzyLeaningForward());
addKeyTime( 4000, 180.0, 75.0, 0.00, new BuzzyLeaningForward());
addKeyTime( 6000, 540.0, 355.0, 0.00, new BuzzyCrouching());
addKeyTime( 6500, 540.0, 355.0, 0.00, new BuzzyStanding());
setEndState(REMAIN);
}
/**
* Add a key time
*
* @param time The key time
* @param x The x position
* @param y The y position
* @param r The rotation angle
* @param content The static visual content
*/
private void addKeyTime(int time, double x, double y,
double r, AggregateContent content)
{
addKeyTime(time, new Point2D.Double(x, y), new Double(r),
new Double(1.0), content);
}
}
package visual.dynamic.described;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.geom.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import app.*;
import visual.*;
import visual.dynamic.described.BuzzyOnMars;
import visual.dynamic.described.Stage;
import visual.statik.sampled.*;
/**
* An example that uses multiple views
*
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
* @version 1.0
*
*/
public class DiptychApp
extends AbstractMultimediaApp
{
/**
* The entry point
*/
public void init()
{
BuzzyOnMars buzzy;
Content mars;
ContentFactory factory;
JFrame window2;
JPanel contentPane;
Stage stage;
VisualizationRenderer renderer1, renderer2;
VisualizationView view1, view2;
// The Stage for Buzzy
stage = new Stage(50);
stage.setBackground(Color.white);
stage.setRestartTime(7000);
view1 = stage.getView();
view1.setRenderer(new PartialVisualizationRenderer(
view1.getRenderer(),
0.0, 0.0));
view1.setBounds(0,0,320,480);
renderer2 = new PartialVisualizationRenderer(
new PlainVisualizationRenderer(), 320.0, 0.0);
view2 = new VisualizationView(stage, renderer2);
view2.setBounds(0,0,320,480);
stage.addView(view2);
factory = new ContentFactory();
mars = factory.createContent("/visual/dynamic/described/mars.gif");
stage.add(mars);
// Buzzy
buzzy = new BuzzyOnMars();
stage.add(buzzy);
// The content pane for the main window
contentPane = (JPanel)rootPaneContainer.getContentPane();
contentPane.add(view1);
// The content pane for the other window
window2 = new JFrame();
window2.setSize(320,480);
contentPane = (JPanel)window2.getContentPane();
contentPane.add(view2);
window2.setVisible(true);
stage.start();
}
}
package visual.dynamic.described;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.geom.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import app.*;
//import gui.*;
import visual.*;
import visual.dynamic.described.Airplane;
import visual.dynamic.described.BuzzyOnMars;
import visual.dynamic.described.Stage;
import visual.statik.sampled.*;
/**
* An example that illustrates the use of multiple views
*
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
* @version 1.0
*
*/
public class PIPApp
extends AbstractMultimediaApp
{
/**
* The entry point
*/
public void init()
{
Airplane plane;
BuzzyOnMars buzzy;
Content mars;
ContentFactory factory;
JPanel contentPane;
Stage stage1, stage2;
VisualizationView view1, view2;
// The Stage for Buzzy
stage1 = new Stage(50);
stage1.setBackground(Color.white);
stage1.setRestartTime(7000);
view1 = stage1.getView();
view1.setRenderer(new ScaledVisualizationRenderer(
view1.getRenderer(),
640.0, 480.0));
view1.setBounds(0,0,640,480);
factory = new ContentFactory();
mars = factory.createContent(
"/visual/dynamic/described/mars.gif");
stage1.add(mars);
// Buzzy
buzzy = new BuzzyOnMars();
stage1.add(buzzy);
// The stage for the airplane
stage2 = new Stage(50);
view2 = stage2.getView();
view2.setRenderer(new ScaledVisualizationRenderer(
view2.getRenderer(),
640.0, 480.0));
view2.setBounds(50,50,160,120);
view2.setSize(160,120);
view2.setBackground(Color.white);
stage2.setRestartTime(12000);
// The Airplane
plane = new Airplane();
stage2.add(plane);
// The content pane
contentPane = (JPanel)rootPaneContainer.getContentPane();
contentPane.add(view2);
contentPane.add(view1);
stage1.start();
stage2.start();
}
}
package visual.dynamic.described;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.geom.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import app.*;
import visual.*;
import visual.dynamic.described.Airplane;
import visual.dynamic.described.BuzzyOnMars;
import visual.dynamic.described.Stage;
import visual.statik.sampled.*;
/**
* An example that illustrates the use of multiple views
*
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
* @version 1.0
*
*/
public class JumboTronApp
extends AbstractMultimediaApp
{
/**
* The entry point
*/
public void init()
{
BuzzyOnMars buzzy;
Content mars;
ContentFactory factory;
JPanel contentPane;
ScaledVisualizationRenderer renderer2;
Stage stage;
VisualizationView view1, view2;
// The Stage for Buzzy
stage = new Stage(50);
stage.setBackground(Color.white);
stage.setRestartTime(7000);
view1 = stage.getView();
view1.setBounds(0,0,640,480);
renderer2 = new ScaledVisualizationRenderer(
new PlainVisualizationRenderer(), 640.0, 480.0);
view2 = new VisualizationView(stage, renderer2);
view2.setBounds(50,50,160,120);
stage.addView(view2);
factory = new ContentFactory();
mars = factory.createContent(
"/visual/dynamic/described/mars.gif");
stage.add(mars);
// Buzzy
buzzy = new BuzzyOnMars();
stage.add(buzzy);
// The content pane
contentPane = (JPanel)rootPaneContainer.getContentPane();
contentPane.add(view2);
contentPane.add(view1);
stage.start();
}
}