|
Implementing State Machines
with Examples in C |
|
Prof. David Bernstein |
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |
|
Implementing State Machines
with Examples in C |
|
Prof. David Bernstein |
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |
hardware.h
#ifndef HARDWARE_H
#define HARDWARE_H
// LED Settings.
typedef enum
{
LED_OFF,
LED_ON,
LED_NUMBER_OF_SETTINGS
} led_setting;
// Motor Settings.
typedef enum
{
MOTOR_CLOSING,
MOTOR_OFF,
MOTOR_OPENING,
MOTOR_NUMBER_OF_SETTINGS
} motor_setting;
// Events.
typedef enum
{
CLOSE_BUTTON_PRESSED,
CLOSED_DETECTED,
OPEN_BUTTON_PRESSED,
OPENED_DETECTED,
NUMBER_OF_EVENTS
} event;
// Control of the LED Indicators.
void
set_closed_indicator(led_setting value);
void
set_opened_indicator(led_setting value);
// Control of the Motor.
void
set_motor(motor_setting value);
#endif
Aside: Enumeration constants have the values \(0, 1, \ldots, n-1\)
which allows us to use the _NUMBER_OF_ idiom.
hardware.c
#include "hardware.h"
// The LED Indicators
void
set_closed_indicator(led_setting value)
{
// Details omitted
}
void
set_opened_indicator(led_setting value)
{
// Details omitted
}
// The Motor
void
set_motor(motor_setting value)
{
// Details omitted
}
Note: All of the functions and enumerations have file scope.
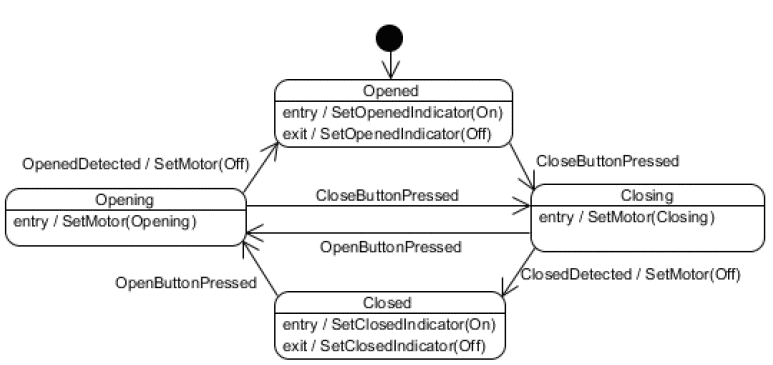
if statementsswitch statements (see below)switch Statementsstatemodel.h
#ifndef STATEMODEL_H
#define STATEMODEL_H
#include "hardware.h"
// The states
typedef enum
{
CLOSED,
CLOSING,
OPENED,
OPENING,
NUMBER_OF_STATES
} state;
// The event handler.
void
handle_event(event current_event);
void
setup_states();
#endif
switch Statements (cont.)statemodel.c
#include "statemodel.h"
// The current state (which is initially OPENED).
static state current_state = OPENED;
// The event handler.
void
handle_event(event current_event)
{
switch(current_state)
{
case CLOSED:
switch(current_event)
{
case OPEN_BUTTON_PRESSED:
set_closed_indicator(LED_OFF); // exit from CLOSED
current_state = OPENING; // transition to OPENING
set_motor(MOTOR_OPENING); // entry to OPENING
break;
}
break;
case CLOSING:
switch (current_event)
{
case CLOSED_DETECTED:
set_motor(MOTOR_OFF); // effect of CLOSED_DETECTED when CLOSING
current_state = CLOSED; // transition to CLOSED
set_closed_indicator(LED_ON); // entry to CLOSED
break;
case OPEN_BUTTON_PRESSED:
current_state = OPENING; // transition to OPENING
set_motor(MOTOR_OPENING); // entry to OPENING
break;
}
break;
case OPENED:
switch (current_event)
{
case CLOSE_BUTTON_PRESSED:
set_opened_indicator(LED_OFF); // exit from OPENED
current_state = CLOSING; // transition to CLOSING
set_motor(MOTOR_CLOSING); // entry to CLOSING
break;
}
break;
case OPENING:
switch (current_event)
{
case CLOSE_BUTTON_PRESSED:
current_state = CLOSING; // transition to CLOSING
set_motor(MOTOR_CLOSING); // entry to CLOSING
break;
case OPENED_DETECTED:
current_state = OPENED; // transition to OPENED
set_opened_indicator(LED_ON); // entry to OPENED
set_motor(MOTOR_OFF); // effect of OPENED_DETECTED when OPENING
break;
}
break;
}
}
Note: current_state has file scope and internal linkage
(because it is decalred to be static)
switch Statementsstruct
is usedstate.h
#ifndef STATE_H
#define STATE_H
// Add an alias: For a type (to the global name space)
// |-type -| |- alias -|
// |-tag-|
typedef struct state state;
// Add an alias: For the event handlers
// |-return type-| |- alias -||- params -|
typedef state* event_handler(void);
// Add an alias: For the actions
typedef void action(void);
// Define the identifier/tag state as a struct.
struct state {
event_handler* close_button_pressed;
event_handler* closed_detected;
event_handler* open_button_pressed;
event_handler* opened_detected;
action* entry_to;
action* exit_from;
};
// Declare variables to hold pointers to the default_event_handler and
// the default_action
extern event_handler* default_event_handler;
extern action* default_action;
// Declare a variable to hold the default_state
// |- type -| |- name -|
// |-tag-|
extern struct state default_state;
// Note: Because of the typedef for the alias state, this could also be:
// extern state default_state;
#endif
Note: default_event_handler, default_action
and default_state are extern because they
must be declared in the scope of each individual state but are defined
in states.c.
state.c
#include "state.h"
#include <stdlib.h> // For NULL
// Define all of the functions that are not exposed
// by the header file.
state*
return_null()
{
return NULL;
}
void
return_void()
{
}
// Define the default_event_handler and default_action
event_handler* default_event_handler = return_null;
action* default_action = return_void;
// Define the default_state
struct state default_state = {
return_null, // close_button_pressed
return_null, // closed_detected
return_null, // open_button_pressed
return_null, // opened_detected
return_void, // entry_to
return_void // exit_from
};
closed.h
#ifndef CLOSED_H #define CLOSED_H #include "state.h" // Declare all of the functions performed when in the closed state. static state* open_button_pressed(); static void entry_to(); static void exit_from(); // Define the closed state and initialize it to the default_state // Note: setup_closed() must be called to complete the definition. struct state closed; #endif
closed.c
#include "closed.h"
#include "hardware.h"
#include "statemodel.h" // For the other states
void
setup_closed()
{
closed = default_state;
closed.open_button_pressed = open_button_pressed;
closed.entry_to = entry_to;
closed.exit_from = exit_from;
}
static state*
open_button_pressed()
{
exit_from();
return &opening;
}
static void
entry_to()
{
set_closed_indicator(LED_ON);
}
static void
exit_from()
{
set_closed_indicator(LED_OFF);
}
statemodel.h
#ifndef STATEMODEL_H #define STATEMODEL_H #include "hardware.h" #include "state.h" // Declare all of the states used in the state model extern state closed; extern state closing; extern state opened; extern state opening; // Declare all of the state setup functions void setup_closed(); void setup_closing(); void setup_opened(); void setup_opening(); // Declare all of the functions used in the state model itself (i.e., // not in the individual states). void setup_states(); void handle_event(event current_event); #endif
Note: Each of the individual states are extern because,
though they are declared here, they are defined in the header files
for the individual states.
statemodel.c
#include "statemodel.h"
#include <stdlib.h> // For NULL
// Define the initial state.
static state* current_state = &opened;
void
setup_states()
{
setup_closed();
setup_closing();
setup_opened();
setup_opening();
}
// Define the functions.
void
handle_event(event current_event)
{
state* next_state;
next_state = NULL;
switch(current_event) // exit current_state and have the appropriate effect
{
case CLOSE_BUTTON_PRESSED:
next_state = current_state-%gt;close_button_pressed();
break;
case CLOSED_DETECTED:
next_state = current_state-%gt;closed_detected();
break;
case OPEN_BUTTON_PRESSED:
next_state = current_state-%gt;open_button_pressed();
break;
case OPENED_DETECTED:
next_state = current_state-%gt;opened_detected();
break;
}
if (next_state != NULL)
{
current_state = next_state; // Change states
current_state-%gt;entry_to(); // enter the new state
}
}
closed.h and
closed.c
switch
statements?