|
Scope, Storage Duration, and Linkage in C
an Introduction |
|
Prof. David Bernstein |
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |
|
Scope, Storage Duration, and Linkage in C
an Introduction |
|
Prof. David Bernstein |
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |
char, int, void)inline)auto,
extern, register,
static)struct, union,
enum)// Type Specifier int i; // Type Specifier with a Modifier double grades[10]; void error_exit(); // Type Specifier with a Type Qualifier volatile int size; // Type Specifier with a Type Qualifier and Modifier const int *fp;
#include <stdio.h>
int
main(void)
{
n += 5;
printf("%d\n", n);
return 0;
}
n is not declared
in the scope of main()
#include <stdio.h>
int n = 0;
int
main(void)
{
n += 5;
printf("%d\n", n);
return 0;
}
n has file scope
#include <stdio.h>
int n = 0;
int
main(void)
{
int n;
n += 5;
printf("%d\n", n);
return 0;
}
n with file
scope and an n with local scope
n is not
initialized.
#include <stdio.h>
int n = 0;
int
main(void)
{
int n = 1;
n += 5;
printf("%d\n", n);
return 0;
}
n with file
scope and an n with local scope
malloc()) and
ends at deallocation (e.g., free())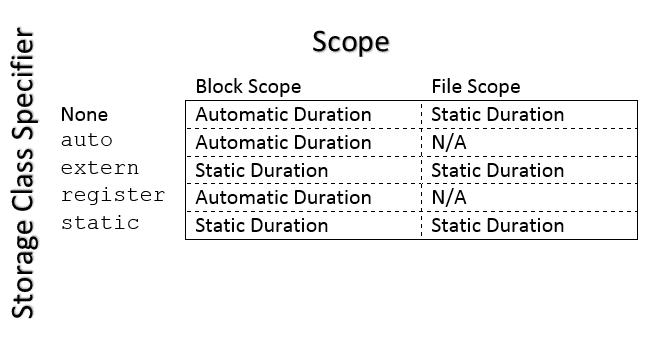
#include <stdio.h>
int
total(int x)
{
static int total = 0;
total += x;
return total;
}
int
main(void)
{
total(5);
total(10);
printf("%d\n", total(15));
return 0;
}
static specifier
can be used in the declaration of a varaible with block scope
library.h
#ifndef LIBRARY_H #define LIBRARY_H int net_price(int price, int discount); static int validate(int n); #endif
library.c
#include "library.h"
int
net_price(int price, int discount)
{
return validate(price - discount);
}
static int
validate(int n)
{
if (n < 0) return 0;
else return n;
}
driver.c
#include "library.h"
int
main(void)
{
int i, j;
i = validate(-5);
j = net_price(6, 2);
}
validate() in
main() is undefined because validate()
has internal linkage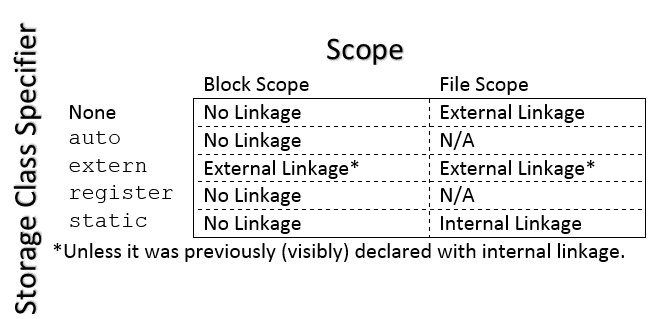
#include <stdio.h>
int n = 0;
int
main(void)
{
extern int n;
n += 5;
printf("%d\n", n);
return 0;
}
// A definition (and implicit declaration) of a function
int
max(int a, int b)
{
if (a > b) return a;
else return b;
}
// A definition (and implicit declaration) of a variable with file scope
int total = 0;
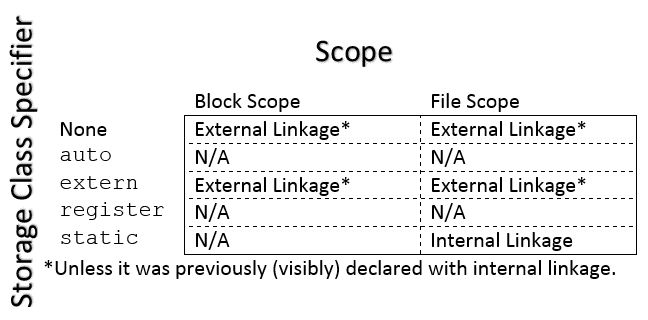
extern == Yes:
extern == No or static == Yes):
= 0 or = {0}
if there is no definition in the same translation
unit)// A declaration with external linkage extern int i; // A definition with external linkage int total = 0; // A definition with internal linkage static const char *university = "JMU"; // A tentative definition with external linkage int j; // A tentative definition with internal linkage static int k;
account.h and
account.c
driver.c that
uses the libraryaccount.h
#ifndef ACCOUNT_H #define ACCOUNT_H #define ACCT_OK 0 #define ACCT_INVALID 1 #define ACCT_CLOSED 2 int acct_status; #endif
account.c
#include "account.h" // Use acct_status
driver.c
#include "account.h" // Use acct_status
account.h is in
both translation unitsmultiple definition of 'acct_status'
because acct_status has been defined in both
translation units
account.h
#ifndef ACCOUNT_H #define ACCOUNT_H #define ACCT_OK 0 #define ACCT_INVALID 1 #define ACCT_CLOSED 2 // Don't define acct_status since that caused the problem #endif
account.c
#include "account.h" // Use acct_status
driver.c
#include "account.h" // Use acct_status
'acct_status' was not declared in this scope
account.h
#ifndef ACCOUNT_H #define ACCOUNT_H #define ACCT_OK 0 #define ACCT_INVALID 1 #define ACCT_CLOSED 2 // Don't define acct_status #endif
account.c
#include "account.h" int acct_status; // Use acct_status
driver.c
#include "account.h" // Use acct_status
account.c will compile but
driver.c won'taccount.h
#ifndef ACCOUNT_H #define ACCOUNT_H #define ACCT_OK 0 #define ACCT_INVALID 1 #define ACCT_CLOSED 2 extern int acct_status; #endif
account.c
#include "account.h" // Use acct_status
driver.c
#include "account.h" // Use acct_status
acct_status
is only declared in account.h, not defined
undefined reference to 'acct_status'
because it has been declared but not defined
account.h
#ifndef ACCOUNT_H #define ACCOUNT_H #define ACCT_OK 0 #define ACCT_INVALID 1 #define ACCT_CLOSED 2 extern int acct_status; #endif
account.c
#include "account.h" int acct_status = ACCT_OK; // Use acct_status
driver.c
#include "account.h" // Use acct_status