|
Using Arrays
An Introduction with Examples in Java |
|
Prof. David Bernstein |
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |
|
Using Arrays
An Introduction with Examples in Java |
|
Prof. David Bernstein |
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |
income1 = 550.75;
income2 = 25.60;
income3 = 347.10;
income4 = 120.45;
income5 = 885.00;
income6 = 10.99;
income7 = 123.45;
An array is a contiguous block of memory that can be used to hold multiple homogeneous elements.
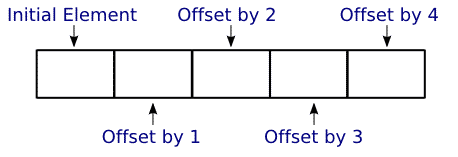
[]
Modifier:
int[] income;
[]
Operator:
income[5] = 250000;
total = income[3];
One can declare an array and assign all of the elements to it using an "array literal" (formally, an array initializer) as follows:
char[] course = {'C','S','1','3','9'};
int[] age = {18, 21, 65};
One can then assign elements or access elements using the []
operator.
One can declare an array and assign default values to all of the elements to it as follows:
char[] course;
int[] age;
course = new char[5];
age = new int[3];
One can then assign elements or access elements using the []
operator.
int[] income;
income = new int[7];
income[0] = 550.75;
income[1] = 25.60;
income[2] = 347.10;
income[3] = 120.45;
income[4] = 885.00;
income[5] = 10.99;
income[6] = 123.45;
ArrayIndexOutOfBounds "error" will be
generated)