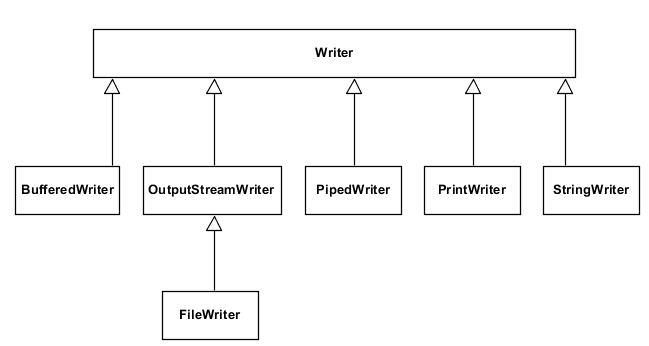
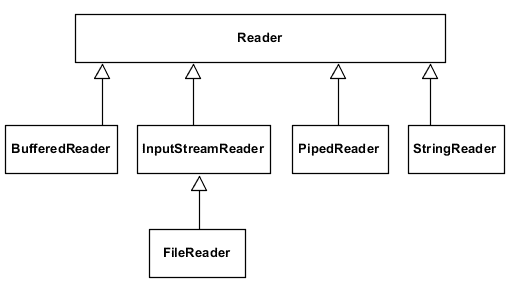
Character Input and Output in Java
Intermediate Topics
|
|
Prof. David Bernstein
James Madison University
|
|
|
Computer Science Department
|
|
bernstdh@jmu.edu
|

A Simple Example



javaexamples/iobasics/WriterReaderExample.java
The Benefits of Decorating Streams



An Example
javaexamples/iobasics/ReaderExample.java
Processing Text Output (cont.)



An Example that Formats "Choices"
javaexamples/iobasics/ChoiceFormatExample.java
Processing Text Output (cont.)



An Example that Formats Numbers
javaexamples/iobasics/NumberFormatExample.java
Processing Input (cont.)



Using the StringTokenizer
javaexamples/iobasics/FacultyRecordTokenizer.java
Processing Input (cont.)



Using the parse___() Methods
javaexamples/iobasics/ExpressionTokenizer.java
Processing Input (cont.)



A Comparison of StringTokenizer and String.split()
javaexamples/iobasics/BufferedReaderExample.java
There's Always More to Learn