

|
Basics of Computer Graphics
in Java |
|
Prof. David Bernstein
|
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |



|
Basics of Computer Graphics
in Java |
|
Prof. David Bernstein
|
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |







setFont method in
Graphics2D


Line Metrics

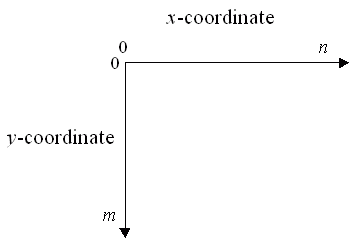
The x and y passed to
drawString(String s, float x, float y) are the left end
of the baseline.


public void paint(Graphics g)
methodJComponent which does very little in its
paint() method
