

|
Direct3D Basics
with Examples in C/C++ |
|
Prof. David Bernstein
|
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |



|
Direct3D Basics
with Examples in C/C++ |
|
Prof. David Bernstein
|
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |





DXUT orHRESULT IDirect3D9::CreateDevice(UINT adapter, D3DDEVTYPE type, HWND window, DWORD flags, D3DPRESENT_PARAMETERS* params, IDirect3DDevice9** returnedDevice)
D3DDEVTYPE_HAL)
D3DDEVTYPE_REF)


D3DCREATE_SOFTWARE_VERTEXPROCESSING
D3DCREATE_HARDWARE_VERTEXPROCESSING
D3DCREATE_MIXED_VERTEXPROCESSING




D3DCOLOR_ARGB)
struct for a vertex
D3DFVF_XYZ
D3DFVF_DIFFUSE,
D3DFVF_SPECULAR
D3DFVF_NORMAL
D3DFVF_PSIZE


IDirect3DVertexBuffer9)
HRESULT CreateVertexBuffer(UINT size, DWORD usage, DWORD fvf, D3DPOOL pool, IDirect3DVertexBuffer9** vertexBuffer, NULL)




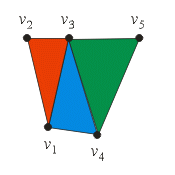
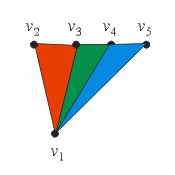


HRESULT IDirect3DDevice9::DrawPrimitive(D3DPRIMITIVETYPE type, UINT startVertex, UINT primitiveCount)
HRESULT IDirect3DDevice9::DrawIndexedPrimitive(D3DPRIMITIVETYPE type, INT offset, UINT minIndex, UINT numVertices, UINT startIndex, UINT count)


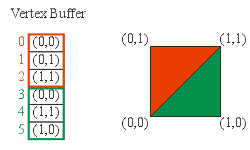
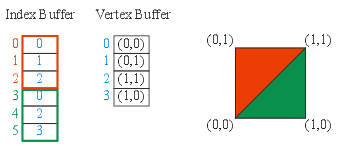


IDirect3DDevice9::BeginScene()
IDirect3DDevice9::EndScene()
IDirect3DDevice9::Present(NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL)


HRESULT IDirect3DDevice9::SetStreamSource(UNIT streamNumber, IDirect3DVertexBuffer9* streamData, UINT offset, UINT stride)
HRESULT IDirect3DDevice9::SetFVF(DWORD fvf)




D3DXMATRIX
D3DXMatrixRotation*(),
D3DXMatrixReflect(),
D3DXMatrixScaling(),
D3DXMatrixTranslation(), etc...
HRESULT IDirect3DDevice9::SetTransform(D3DTRANSFORMSTATETYPE type, CONST D3DMATRIX* m)
type is D3DTS_VIEW,
D3DTS_PROJECTION, or D3DTS_WORLD


D3DXMATRIX* D3DXMatrixLookAtLH(D3DXMATRIX* mOut, CONST D3DXVECTOR3* eye, CONST D3DXVECTOR3* at, CONST D3DXVECTOR3* up) where the
LH indicates "left-handed"
D3DXMATRIX* D3DXMatrixRotationYawPitchRoll(D3DXMATRIX* mOut,FLOAT yaw, FLOAT pitch, FLOAT roll)
where the pitch is around \(x\), the yaw is around \(y\), and the roll is around \(z\)


D3DXMATRIX* D3DXMatrixOrthoLH(D3DXMATRIX* mOut, FLOAT w, FLOAT h, FLOAT znear, FLOAT zfar)
D3DXMATRIX* D3DXMatrixPerspectiveFovLH(D3DXMATRIX* mOut, FLOAT fovy, FLOAT aspect, FLOAT znear, FLOAT zfar)



