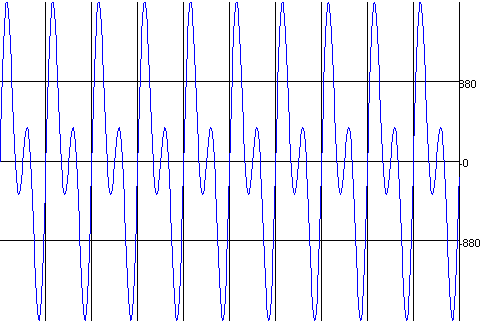
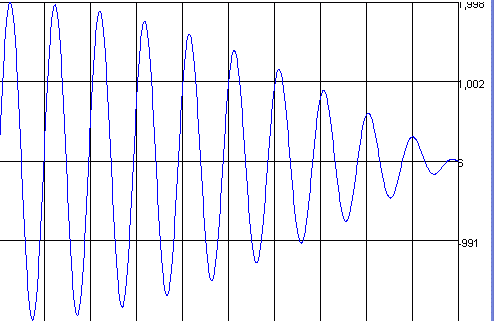
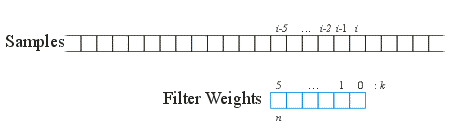
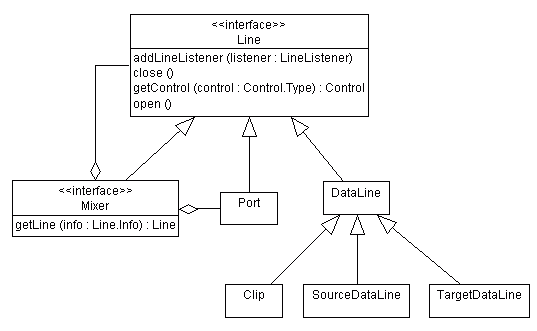
|
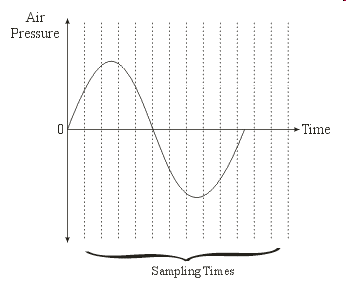
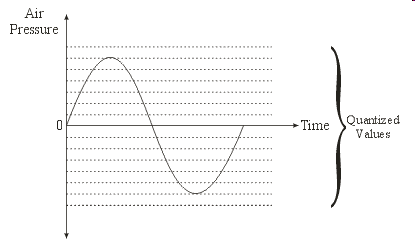
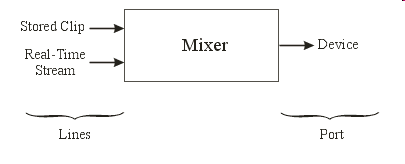
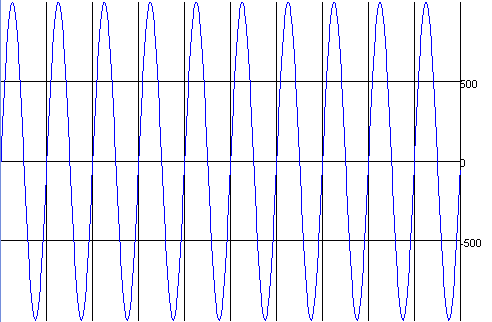
Sampled Auditory Content
An Introduction with Examples in Java |
|
Prof. David Bernstein
|
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |