
interface
and a class (in Java).
interface
and an abstract class (in Java).
| (1) | _____ |
An interface can be thought of as a contract. |
| (2) | _____ |
As we have used the term this semester, "polymorphism" means "used in a variety of different object-oriented languages". |
| (3) | _____ |
One interface can extend another interface (in Java). |
| (4) | _____ |
It is possible to create instances of an abstract class. |
| (5) | _____ |
An abstract class can implement an interface. |
Image and
JPEG classes:
public abstract class Image
{
protected int[] bytes;
public void Image(int w, int h)
{
bytes = new int[w*h];
}
public abstract void paint();
}
public class JPEG extends Image
{
public int width, height;
public JPEG(int w, int h)
{
super(w, h);
width = w;
height = h;
}
public void paint()
{
int i;
for (i=0; i<bytes.length; i++) {
System.out.println(bytes[i]);
}
}
}
identify the problem(s) with the following code snippet:
public class Bad
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Image copyCat;
JPEG cat;
cat = new JPEG(100, 20);
System.out.println("Width of cat: "+cat.w);
System.out.println("Height of cat: "+cat.h);
cat.paint(this);
copyCat = cat;
}
}
Security and Stock classes:
public abstract class Security
{
protected double price;
private int volume;
public Security()
{
price = 100.0;
volume = 5000;
}
public abstract void print();
}
public class Stock extends Security
{
private String exchange;
public Stock()
{
super();
price = 200.0;
exchange = new String("NASDAQ");
}
public void print()
{
System.out.println(price+" "+exchange);
}
}
What will be printed by the following code snippet?
public class Question
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Stock s;
s = new Stock();
s.print();
}
}
Clock class:
public abstract class Clock
{
protected int hours, minutes;
public Clock()
{
this(0,0);
}
public Clock(int hours, int minutes)
{
this.hours = hours;
this.minutes = minutes;
}
public abstract String format();
public void print()
{
System.out.println(format());
}
}
the following TerseClock class:
public class TerseClock extends Clock
{
public TerseClock(int hours, int minutes)
{
super(hours, minutes);
}
public String format()
{
return "" + hours + ":" + minutes;
}
}
and the following VerboseClock class:
public class VerboseClock extends Clock
{
public VerboseClock(int hours, int minutes)
{
super(hours, minutes);
}
public String format()
{
return "The time is " + minutes +" after " + hours;
}
}
either identify and fix all of the errors
in the following ClockDriver class
or show what will be printed (assuming it is executed properly):
public class ClockDriver
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Clock c;
c = new TerseClock(10,15);
c.print();
c = new VerboseClock(12,30);
c.print();
}
}
Taxable interface,
and Book, Clothes, Food,
and TaxBasedOnPrice classes:
public interface Taxable
{
public abstract double getTax();
}
public class Book implements Taxable
{
private String title;
public Book(String title)
{
this.title = title;
}
public double getTax()
{
return 5.00;
}
public String toString()
{
return title + " Tax: " + getTax();
}
}
public class Clothes extends TaxBasedOnPrice
{
private int size;
private String color, style;
public Clothes(String style, String color, int size, double price)
{
super(price, 0.10);
this.style = style;
this.color = color;
this.size = size;
}
public String toString()
{
return "Size " + size + " " + style + " in " + color +
" Price: " + getPrice() + " Tax: " + getTax();
}
}
public class Food extends TaxBasedOnPrice
{
private String description;
public Food(String description, double price)
{
super(price, 0.05);
this.description = description;
}
public String toString()
{
return description + " Price: " + getPrice() +
" Tax: " + getTax();
}
}
public abstract class TaxBasedOnPrice implements Taxable
{
private double price, taxRate;
public TaxBasedOnPrice(double price, double taxRate)
{
this.price = price;
this.taxRate = taxRate;
}
public double getPrice()
{
return price;
}
public double getTax()
{
return price * taxRate;
}
}
what will be printed by the following driver?
public class TaxDriver
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Book book;
Clothes clothes;
Food food;
Taxable[] purchases;
purchases = new Taxable[3];
book = new Book("Multimedia Software");
clothes = new Clothes("Shirt", "Yellow", 8, 12.00);
food = new Food("Hot Dog",2.00);
purchases[0] = book;
purchases[1] = clothes;
purchases[2] = food;
printMessage(food);
printMessage(purchases[0]);
printMessage(clothes);
printMessage(purchases[1]);
System.out.println(book.getTax());
System.out.println(clothes.getTax());
System.out.println(food.getTax());
for (int i=0; i<purchases.length; i++)
System.out.println(purchases[i].getTax());
printAll(purchases);
}
public static void printMessage(Food food)
{
System.out.println("I'm food!");
}
public static void printMessage(Taxable taxable)
{
System.out.println("I'm taxable!");
}
public static void printAll(Taxable[] items)
{
for (int i=0; i<items.length; i++)
System.out.println(items[i].getTax());
for (int i=0; i<items.length; i++)
System.out.println(items[i].toString());
}
}
TwoPartMeasure class and the
following Length class:
/**
* A two-part measurement (e.g., a length in feet and inches, a
* weight in pounds and ounces, ...)
*
* A two-part measurement consists of a number of
* large units (e.g., feet) and a number of small
* units (e.g., inches)
*/
1 public abstract class TwoPartMeasure
2 {
3 private int large, sign, small;
4 protected int smallsPerLarge;
5 protected String largeUnitsSingular, largeUnitsPlural;
6 protected String smallUnitsSingular, smallUnitsPlural;
/**
* Default Constructor
*/
7 public TwoPartMeasure()
8 {
9 this(0, 0, true);
10 }
/**
* Explicit Value Constructor
*
* @param large The number of large units (must be positive)
* @param small The number of small units (must be positive)
*/
11 public TwoPartMeasure(int large, int small)
12 {
13 this(large, small, true);
14 }
/**
* Explicit Value Constructor
*
* @param large The number of large units (must be positive)
* @param small The number of small units (must be positive)
* @param positive true for positive and false for negative
*/
15 public TwoPartMeasure(int large, int small, boolean positive)
16 {
17 this.large = Math.abs(large);
18 this.small = Math.abs(small);
19 this.sign = 1;
20 if (!positive) this.sign = -1;
21 initializeUnits();
22 }
/**
* Change this TwoPartMeasure by a given amount
*
* @param other The amount to change this TwoPartMeasure by
*/
23 public void changeBy(TwoPartMeasure other)
24 {
25 int otherTotal, thisTotal, total;
26 otherTotal = other.toSmall();
27 thisTotal = this.toSmall();
28 total = thisTotal + otherTotal;
29 large = total / smallsPerLarge;
30 small = total % smallsPerLarge;
31 }
/**
* Check to see if thisTwoPartMeasure is equal to
* a given TwoPartMeasure
*
* @param other The other TwoPartMeasure use in the comparison
* @return true if the two are equal and false otherwise
*/
32 public boolean equals(TwoPartMeasure other)
33 {
34 boolean comparison;
35 int otherTotal, thisTotal;
36 thisTotal = this.toSmall();
37 otherTotal = other.toSmall();
38 comparison = false;
39 if (thisTotal == otherTotal) comparison = true;
40 return comparison;
41 }
/**
* Initialize the "constants" used by a TwoPartMeasure,
* specifically:
*
* smallsPerLarge (e.g., inches per foot, ounces per pound)
* largeUnitsSingular (e.g., "foot", "pound")
* largeUnitsPlural (e.g., "feet", "pounds")
* smallUnitsSingular (e.g., "inch", "ounce")
* smallUnitsPlural (e.g., "inches", "ounces")
*/
42 protected abstract void initializeUnits();
/**
* "Convert" this TwoPartMeasure to small units
* (e.g., from 5 feet 7 inches to 67 inches)
*
* @return The value in small units
*/
43 private int toSmall()
44 {
45 int total;
46 total = sign * ((large * smallsPerLarge) + small);
47 return total;
48 }
/**
* Get a String representation of this Length
*
* @return The String
*/
49 public String toString()
50 {
51 String s;
52 s = new String();
53 if (sign < 0) s += "Negative ";
54 if (large == 1) s += large + " " + largeUnitsSingular;
55 else s += large + " " + largeUnitsPlural;
56 if (small == 1) s += " " + small + " " + smallUnitsSingular;
57 else s += " " + small + " " + smallUnitsPlural;
58 return s;
59 }
60 }
/**
* A length in traditional U.S. units (i.e., feet and inches)
*/
1 public class Length extends TwoPartMeasure
2 {
/**
* Default Constructor
*/
3 public Length()
4 {
5 super(0, 0, true);
6 }
/**
* Explicit Value Constructor
*
* @param feet The number of feet (must be positive)
* @param inches The number of inches (must be positive)
*/
7 public Length(int feet, int inches)
8 {
9 super(feet, inches, true);
10 }
/**
* Explicit Value Constructor
*
* @param feet The number of feet (must be positive)
* @param inches The number of inches (must be positive)
* @param positive true for a positive length, false for negative
*/
11 public Length(int feet, int inches, boolean positive)
12 {
13 super(feet, inches, positive);
14 }
15 }
what compile-time error will be generated if:
TwoPartMeasure and
compile TwoPartMeasure?
abstract from line 42 in
TwoPartMeasure and compile TwoPartMeasure?
Length class?
TwoPartMeasure
and Length classes above. What is good about the
design and what is bad about it?
DirectoryComparator,
DirectoryNameComparator, and
DirectorySizeComparator classes described in the
following UML diagram (where the + indicates that the
method/attribute is public, the # indiciates that the method/attribute
is protected, and italics indicates that the method/class is abstract):
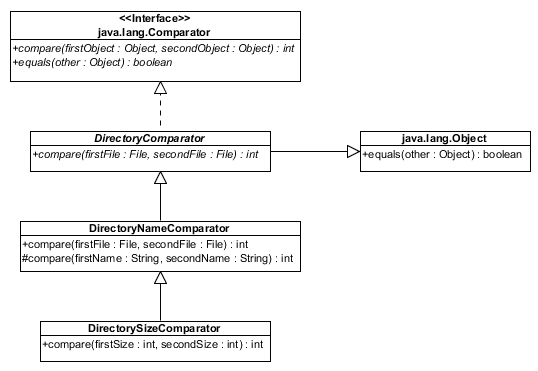
Note: In the diagram above, subclasses (and classes that implement interfaces) do not explicitly list the methods that they must implement or that they inherit. On the other hand, when a subclass contains a method with the same signature as a method in the super class, that method in the subclass overrides the version in the superclass.
public abstract class Policy
{
protected double deductable;
protected String policyHolder;
// Details Omitted
}
public class IndividualPolicy extends Policy
{
private int yearsAsCustomer;
// Details Omitted
}
public class FamilyPolicy extends Policy
{
private String[] others;
// Details Omitted
}
You must add functionality that would allow both
IndividualPolicy and FamilyPolicy objects
to correctly respond to getCopay() messages. In
response to such a message, an IndividualPolicy object
must return a double that has the value
deductable / 10.0 + 15.0 and a
FamilyPolicy object must return a double
that has the value (deductable / 10.0 + 15.0) * 1.5 +
(others.length * 5.0). Note: Better answers have less code
duplication and take advantage of the class hierarchy.
Numberizer class:
public class Numberizer
{
public double cool(double x, double guess)
{
double value;
if (Math.abs(x/guess-guess) < 0.001)
{
value = guess;
}
else
{
value = cool(x, (guess+x/guess)/2.0);
}
return value;
}
public double radical(double x)
{
return cool(x, 1.0);
}
}
carefully trace the execution of the following:
public class NumberizerDriver
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Numberizer numb;
numb = new Numberizer();
System.out.println("2: "+numb.radical(2.0));
}
}
MindNumber class:
public class MindNumber
{
public static int numb(int i)
{
int result;
if (i < 1)
{
result = -1;
}
else if (i < 10)
{
result = numb(i-1) + numb(i-2);
}
else if (i%2 == 0)
{
result = numb(i/2);
}
else
{
result = numb(i/2) + numb(i%2);
}
return result;
}
}
carefully trace the execution of the following:
public class MindNumberDriver
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int i;
i = MindNumber.numb(12);
System.out.println(i);
}
}
You may submit your stack of "activation records". If you do, please submit them in the order in which they were created.
enum)
for the playing cards used in poker.
Implement the following method that approximates the value of
e using the equation above. Your method must be
recursive. You should assume that you have a method
int factorial(int n) that calculates the factorial
of n.
/*
* Finds an n-term approximation of e
*
* @param n The number of terms in the summation
* @return The approximation of e
*/
public double e(int n)
{
}
n. Your method must be recursive.
/*
* Finds the factorial of an integer
*
* @param n The integer of interest
* @return The factorial of n
*/
public int factorial(int n)
{
}
public static boolean something(String source, String letter)
{
boolean hit;
String first;
if (source.length() == 0) return true;
first = source.substring(0,1);
hit = (first.equals(letter));
return hit && something(source.substring(1), letter);
}
Numberizer class above.
Copyright 2011