
*******************************
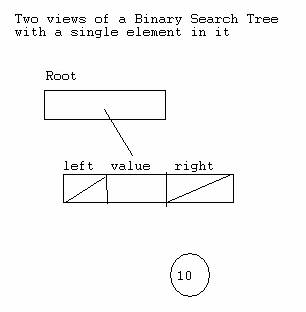
*********************************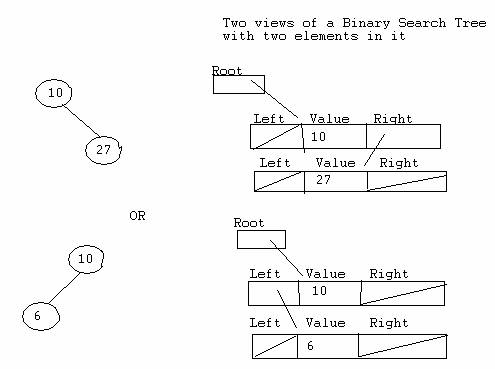
*******************************************************
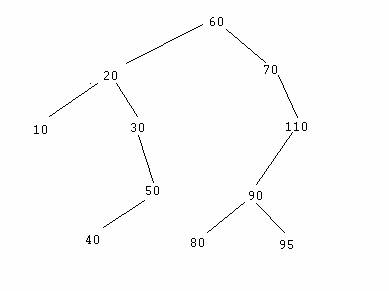
A tree with more nodes
**********************************************
To summarize, complete and clarify our discussion: - here’s one deletion algorithm
Procedure delete searches for the node that contains the key value to be deleted from the tree (i.e. the target node).
If it finds it
- If the target node has an empty subtree (i.e. is a leaf), the target node is removed from the tree
- If the target node does not have a right child, then the node’s left child replaces the node in the tree.
- If the target node does not have a left child, then the node’s right child replaces the node in the tree.
- If the target node has two children, then the value in the target node is replaced by the value in the node in its left subtree with the largest value and then replacing the node containing that value by its left child
Else
- Key value not found
***********************************************************
Make sure you understand the above steps BEFORE doing any coding and try them all on the original tree above
- Delete 80
- Delete 110
- Delete 60
******************************************************
Here’s another idea for step 4 above
- If the target node has two children, attach the right subtree in place of the deleted node and then hang the left subtree onto an appropriate node of the right subtree. (To which node of the right subtree should the former left subtree be attached? Since every key in the left subtree precedes every key of the right subtree, it must be as far to the left as possible, and this point can be found by taking left branches until an empty left subtree is found).
*****************************************************
Before you code, draw additional trees and delete nodes in different places making sure that you understand steps 1 through 3 and both step 4s of the algorithm