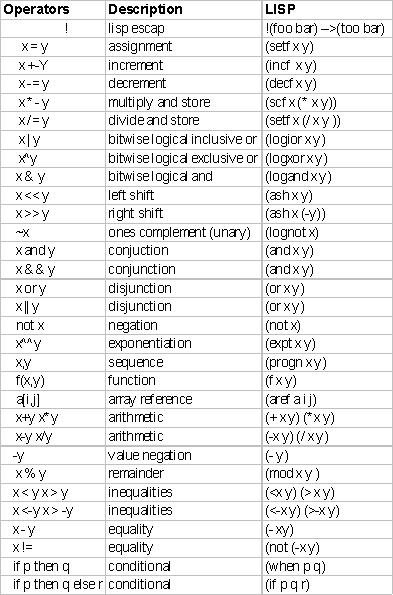
LISP SYNTAX SUMMARY
Parag Patel
Laura Warrener
Scott Doucett
Mike Rodosti
Chirag Patel
|
|
|
Declaration DECLARATION |
|
Syntax: |
|
(declaration name*) |
|
Function: YES-OR-NO-P (&optional (format-string nil) &rest args) |
|
Package:LISP |
|
Asks the user a question
whose answer is either 'YES' or 'NO'. If FORMAT- STRING is non-NIL, then
FRESH-LINE operation is performed, a message is printed as if FORMAT-STRING
and ARGs were given to FORMAT, and then a prompt "(Yes or No)" is
printed. Otherwise, no prompt will appear |
|
Function: EQ (x y) |
|
Package:LISP Returns T if X and Y are the
same identical object; NIL otherwise. |
|
Function: EQUALP (x y) |
|
Package:LISP |
|
Returns T if X and Y are
EQUAL, if they are characters and satisfy CHAR-EQUAL, if they are numbers and
have the same numerical value, or if they have components that are all
EQUALP. Returns NIL otherwise. |
|
Function: EQUAL (x y) |
|
Package:LISP |
|
Returns T if X and Y are EQL
or if they are of the same type and corresponding components are EQUAL.
Returns NIL otherwise. Strings and bit-vectors are EQUAL if they are the same
length and have identical components. Other arrays must be EQ to be EQUAL. |
|
Special Form: |
|
Package:LISP |
|
Syntax: |
|
(loop {form}*) |
|
Executes FORMs repeatedly
until exited by a THROW or RETURN. The FORMs are surrounded by an implicit
NIL block. |
|
Data
Types |
|
------------------ |
|
Numbers: integers and floats, ie. 1, 2, 2.72,
3.14 |
|
Strings: any test enclosed in quotes, ie.
"abc", "1", "hello world" |
|
Characters: a,b,...,z,A,B,...,Z,0,1,...,9,_,-,+,* |
|
Symbols: any sequence of characters, symbols
are case insensitive |
|
`;'
Comment character, everything from the ';' to the end of line is
ignored |
|
FUNCTIONS |
|
Function calls are special lists. |
|
The Function name is either a symbol | + | - |
* |
|
The first item in the function list is the
function name, followed by it's arguments |
|
For example, the function to a add 3 numbers
is: (+ 1 2 3) |
|
Function declarations are in the form: |
|
(DEFUN name (argument_list) expression) |
|
The function returns the last expression in
the expression list. |
|
example functions: |
|
(DEFUN sqr (x) (* x x)) ;
will return the result of the call to '*' |
|
(DEFUN myfunction (x) y) ;
will return the value of 'y' |
|
COMMON
FUNCTIONS |
|
Common Boolean functions returning either T
for true or NIL for false. |
|
(ODDP x) ;
Returns T if x is an odd number |
|
(EVENP x) ;
Returns T if x is an even number |
|
(< x y) ;
Returns T if x is less than y |
|
(= x y) ;
Returns T if x is equal to y |
|
(OR x y) ;
Returns T if x or y is true |
|
(AND x y) ;
Returns T if x and y are true |
|
(NOT x) ;
Returns T if x is not true |
|
CONDITIONALS |
|
(if test_expression true_expression
false_expression) |
|
VARIABLES |
|
(setq x 1) ;
Stores the decimal value 1 into a symbol named "x" |
|
(setq x (+ y z)) ; Stores the result of the add function into "x" |
|
;; QUOTE forces the symbol name to be used
instead of it's storage |
|
(quote my_variable) |
|
'my_variable ;
Shorthand version |
|
LISTS
(setq my_list (LIST 1 2 3 4)) ; build a new list containing 1 thru 4 |
|
(FIRST my_list) ; Returns the first element in
the list ie. '1' |
|
(SECOND my_list) ; Returns the second element in the list ie. '2' |
|
(REST my_list) ;
Returns all but the first ie. '2 3 4' |
|
(EQUAL my_list list2) ; Boolean compare of 2 lists |
|
(EQ my_list list2) ; shorthand of EQUAL |
|
Primitive
functions |
|
CAAR
First element of the first element |
|
CADR
Second element |
|
CDAR
Rest of the element |
|
CDDR
Rest after the second element |
|
CADDR
Third element |
|
CDDDR
Rest after the third element |
|
CADDDR
Fourth element |
|
CDDDDR
Rest after the fourth element |