Printed Names: _______________
_______________
_______________
|
|
|
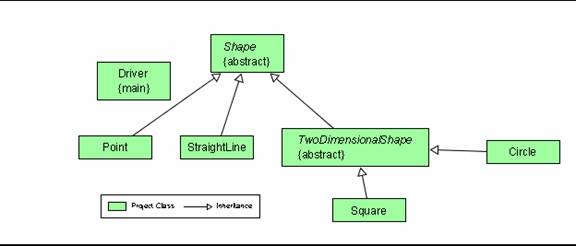
No we cannot instantiate a Shape. |
|
We cannot instantiate a Shap because Shape is an abstract class. If we try, we get the following message Ï ¼§ÏDriver.java:8:
Shape is abstract; cannot be instantiated |
|
Yes abstract classes can have instance variables (class attributes) |
|
Yes abstract classes can have class variables (static variables) |
|
They share the attribute description which, because it’s private, cannot be accessed using super.description , but which can be accessed using the toString method. |
|
The separate attributes are: radius in Circle and side in Square. |
|
|
They are not required to override the toString method because it is not abstract. |
|
Yes, the children of TwoDimensionalShape are required to override the get Area method. |
|
They are required to override the getArea method because it’s abstract. |
|
A good structure to use would be an array of Shape |
|
Shape [ ] myShapes; myShapes = new Shape[5]; |
|
An alternate structure would be an array of TwoDimensionalShape |
|
TwoDimensionalShape [ ] myTwoDimensionalShapes; myTwoDimensionalShapes = new TwoDimensionalShape [5]; |
|
The term for the java feature that allows us to declare
either a TwoDimensionalShape or a Shape object and then choose to make it a
Circle or a Square is polymorphism |
|
myShape[0] = new Circle (3.4); myShape[1] = new Circle (43.7); myShape[2] = new Circle (13.8); myShape[3] = new Square (5.0); myShape [4] = new Square (7.8); |
|
ÏÏÏPoint
coordinates are: 3 and 4 |
|
System.out.println (aBunchOfShapes[1]); |