JMU - CS239 - Preparing for Exam 2
Advanced Programming - CS239
Department of Computer Science
Preparing for Exam 2
What to Expect: This exam will focus on inheritance, polymorphism, abstract classes, interfaces, and recursion. However, to answer these questions you will need to understand the topics covered on the first exam.
You should expect three types of questions: short answer (e.g., true/false, matching, fill-in, multiple choice), code understanding (e.g., error identification, execution tracing), and code development (e.g., method/class writing, test writing).
What to Study: Obviously, you should study the lectures, labs, and reading. However, you should pay particular attention to the labs since there are likely to be questions on the exam like those covered in the labs.
Reading
Responsibility: Everything from Exam 1 plus: Chapter 7 (7.0-7.5), 5.5, Chapter 11 (11.0 – 11.2). Any of the exceptions from Appendix K that
we have seen or discussed in class(think PA2).
Sample Questions
for Exam 2: The questions below are illustrative of the kinds of questions that will be on the
exam. The exam itself may contain
either more or fewer questions.
1. Indicate whether each of the following statements is true or false:
1.
____ An interface can be thought of as a contract.
____ William Loftus is one of the authors of the primary textbook
we are using in CS239 this semester.
____ As we have used the term this semester, "polymorphism" means
"used in a variety of different object-oriented languages".
____ One interface can extend another interface.
____ It is possible to create instances of an abstract class.
2. Given the following Image and JPEG classes:
public abstract class Image
{
protected int[] bytes;
public void Image(int w, int h)
{
bytes = new int[w*h];
}
public abstract void paint();
}
public class JPEG extends Image
{
public int width, height;
public JPEG(int w, int h)
{
super(w, h);
width = w;
height = h;
}
public void paint()
{
int i;
for (i=0; i<bytes.length; i++)
{
System.out.println(bytes[i]);
}
}
}
identify the problem(s) with the following
code snippet:
public class Bad
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Image copyCat;
JPEG cat;
cat = new JPEG(100, 20);
System.out.println("Width of cat: "+ cat.w);
System.out.println("Height of cat: "+ cat.h);
cat.paint(this);
copyCat = cat;
}
}
3. Given the following
/**
* A two-part measurement (e.g., a length in feet and inches, a
* weight in pounds and ounces, ...)
*
* A two-part measurement consists of a number of
* large units (e.g., feet) and a number of small
* units (e.g., inches)
*/
1 public abstract class TwoPartMeasure
2 {
3 private int large, sign, small;
4 protected int smallsPerLarge;
5 protected String largeUnitsSingular, largeUnitsPlural;
6 protected String smallUnitsSingular, smallUnitsPlural;
/**
* Default Constructor
*/
7 public TwoPartMeasure()
8 {
9 this(0, 0, true);
10 }
/**
* Explicit Value Constructor
*
* @param large The number of large units (must be positive)
* @param small The number of small units (must be positive)
*/
11 public TwoPartMeasure(int large, int small)
12 {
13 this(large, small, true);
14 }
/**
* Explicit Value Constructor
*
* @param large The number of large units (must be positive)
* @param small The number of small units (must be positive)
* @param positive true for positive and false for negative
*/
15 public TwoPartMeasure(int large, int small, boolean positive)
16 {
17 this.large = Math.abs(large);
18 this.small = Math.abs(small);
19 this.sign = 1;
20 if (!positive) this.sign = -1;
21 initializeUnits();
22 }
/**
* Change this TwoPartMeasure by a given amount
*
* @param other The amount to change this TwoPartMeasure by
*/
23 public void changeBy(TwoPartMeasure other)
24 {
25 int otherTotal, thisTotal, total;
26 otherTotal = other.toSmall();
27 thisTotal = this.toSmall();
28 total = thisTotal + otherTotal;
29 large = total / smallsPerLarge;
30 small = total % smallsPerLarge;
31 }
/**
* Check to see if thisTwoPartMeasure is equal to
* a given TwoPartMeasure
*
* @param other The other TwoPartMeasure use in the comparison
* @return true if the two are equal and false otherwise
*/
32 public boolean equals(TwoPartMeasure other)
33 {
34 boolean comparison;
35 int otherTotal, thisTotal;
36 thisTotal = this.toSmall();
37 otherTotal = other.toSmall();
38 comparison = false;
39 if (thisTotal == otherTotal) comparison = true;
40 return comparison;
41 }
/**
* Initialize the "constants" used by a TwoPartMeasure,
* specifically:
*
* smallsPerLarge (e.g., inches per foot, ounces per pound)
* largeUnitsSingular (e.g., "foot", "pound")
* largeUnitsPlural (e.g., "feet", "pounds")
* smallUnitsSingular (e.g., "inch", "ounce")
* smallUnitsPlural (e.g., "inches", "ounces")
*/
42 protected abstract void initializeUnits();
/**
* "Convert" this TwoPartMeasure to small units
* (e.g., from 5 feet 7 inches to 67 inches)
*
* @return The value in small units
*/
43 private int toSmall()
44 {
45 int total;
46 total = sign * ((large * smallsPerLarge) + small);
47 return total;
48 }
/**
* Get a String representation of this Length
*
* @return The String
*/
49 public String toString()
50 {
51 String s;
52 s = new String();
53 if (sign < 0)
s = s + "Negative ";
54 if (large == 1)
s = s + large + " " + largeUnitsSingular;
55 else
s = s + large + " " + largeUnitsPlural;
56 if (small == 1)
s = s + " " + small + " " + smallUnitsSingular;
57 else
s = s + " " + small + " " + smallUnitsPlural;
58 return s;
59 }
60 }
/**
* A length in traditional U.S. units (i.e., feet and inches)
*/
1 public class Length extends TwoPartMeasure
2 {
/**
* Default Constructor
*/
3 public Length()
4 {
5 super(0, 0, true);
6 }
/**
* Explicit Value Constructor
*
* @param feet The number of feet (must be positive)
* @param inches The number of inches (must be positive)
*/
7 public Length(int feet, int inches)
8 {
9 super(feet, inches, true);
10 }
/**
* Explicit Value Constructor
*
* @param feet The number of feet (must be positive)
* @param inches The number of inches (must be positive)
* @param positive true for a positive length, false for negative
*/
11 public Length(int feet, int inches, boolean positive)
12 {
13 super(feet, inches, positive);
14 }
15 }
what compile-time
error will be generated if:
you compile the Length class?
you remove the modifier abstract from line 42 in TwoPartMeasure and compile TwoPartMeasure?
you remove line 42 in TwoPartMeasure and compile TwoPartMeasure?
4. Stub-out the DirectoryComparator, DirectoryNameComparator, and DirectorySizeComparator classes described in the following UML diagram:
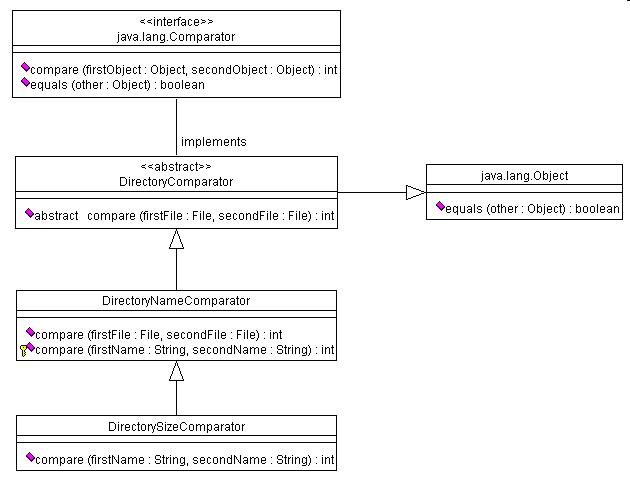
Note: In the diagram above, subclasses (and classes that implement
interfaces) do not explicitly list the methods that they must implement
or that they inherit. On the other hand, when a subclass contains a
method with the same signature as a method in the super class, that
method in the subclass overrides the version in the superclass.
5. Given the following Numberizer class:
public class Numberizer
{
public double cool(double x, double guess)
{
double value;
if (Math.abs(x/guess-guess) < 0.001)
{
value = guess;
}
else
{
value = cool(x, (guess+x/guess)/2.0);
}
return value;
}
public double radical(double x)
{
return cool(x, 1.0);
}
}
carefully trace the execution of the
following:
public class NumberizerDriver
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Numberizer numb;
numb = new Numberizer();
System.out.println("2: "+numb.radical(2.0));
}
}
6. Write a driver that can be used to test the following classes:
public
abstract class Person
{
protected
String id, name;
public Person(String name, String id)
{
this.name = name;
this.id = id;
}
public abstract String getSummary();
}
public class Faculty extends Person
{
private String title;
public Faculty(String name, String id,
String title)
{
super(name, id);
this.title = title;
}
public String getSummary()
{
String info;
info = title + " " +
name;
return info;
}
public void setTitle(String title)
{
this.title = title;
}
}
public class Student extends Person
{
private int credits;
public Student(String name, String id)
{
super(name, id);
credits = 0;
}
public String getSummary()
{
String info;
info = name + "," +
credits + " credits completed";
return info;
}
public void setCredits(int credits)
{
this.credits = credits;
}
}
7. An n-term approximation of the value of e is:
e = 1 + 1/1! + 1/2! + 1/3! + ... + 1/n!
Implement the following method that approximates the value of e using
the equation above. Your method must be recursive.
/*
* Finds an n-term approximation of e
*
* @param n The number of terms in the summation
* @return The approximation of e
*/
Copyright © 2004